Exam 2 Flashcards
(201 cards)
what is this test?

thomas test:
Positive when there is a contraction or contracture of the psoas muscle
- norm = extended leg should contact table
- space = iliopsoas spasm
Test both sides

Tentorium Cerebelli
anterio borderr: clinoid processes - cradles pituitary wiht infundibulum piercing fascia
medial border: anterior clinoid
lateral border: posterior clinoid
cranial rhythmic impulse creates motion of “tent”

how to differentiation b/w disc herniation and piriformis syndrome?
EMG
disc = N impinge prox to piriformis
piuriformis: abnorm distal to piriformis
Articulations lumbar spine
Zygapophoseal joints: (synovial joint).
Intervertebral joints: (Fibrocartilagenous joints.)
interstitial fluid pressure and lymph sys
approximately -6.3mmHg and flow at 120cc/hr
incrase in interstitial P –> increases absorption into cap
if P > 0 = collapse lymph caps
IV disc components
- Fibrocartilaginous joint
- Annulus fibrosis
- thicker anteriorly and thinner posteriorly.
- Nucleus pulposus
- Interlocking crosshatch
- allows the disc to undergo rotary motions and shearing forces while still maintaining restrictive stability.
•Attachment to anterior & posterior longitudinal ligaments
Extension of a vertebral unit causes what on the IV disc and ligaments
Increases pressure on the anterior annulus and ALL
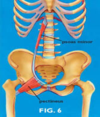
Functional Anatomy-Psoas Major
- Origin –TP/SP/IV discs T12-L5
- Insertion – lesser trochanter
- Innervations- L1-L3
- Actions-Flexes thigh, external rotation, flexes spine on pelvis
taut band
hypercontracted extrafusal muscle fibers
pressed = referred pain, motor dysfunction, autonomic phenom
needling/rolling = local twitch response
Pathophysiology – Psoas Syndrome
M is position of strain and then suddenly lengthens
CNS senses “overstretch” –> reflex contraction
- inc in alpha moto output = incr in gamma firing
pain-spasm feedback loop –> psoas syndrome
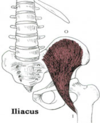
Pelvic Diaphragm
levator ani - 3 M
Coccygeus - 3 M, posterior to levator ani

Piriformis Syndrome
Physical Exam - motion testing, neuro, special tests
motion:
- hip pain with external rotation, passive internal rotation/flex/adduc
- lumbar spine restricted esp in ext
neuro:
- NORMAL!!
special tests:
- SLR (straight leg raising) - painful throughout
gluteus medius: N and spinal lvl
sperior gluteal, L4-5, S1
spondylolysis
stress fx b/w pars interarticularis b/w facets usu L4/L5
most common low back pain in adol athletes
angle & pull of M —> “slippery slope” spondylolisthesis
diseases that increase interstitial P > 0 mmHg
sys htn
cirrhosis
hypoalbuminemia: starvation
toxins
Spondylolisthesis: 80% will present with
hamstring hypertonia
Piriformis Syndrome
OMT - indirect techniques
used more commonly
counterstain: TP at midpole sacrum, piriformis M, postermedial troch
facilitated positional release (FPR)
thymus
loc: superior mediastinum
T-lymphocytes
involution in adulthood
sibson’s fasica
prevert fascia + scalene fascia
thoracic duct txverses sibsons –> C7 and then turns around an emptys into L subclavian
Quadratus Lumborum
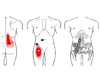
Trigger Points and Referred Pain Patterns

load on L3: in order of increasing load:
bending sideways, standing, twisting
standing (700) < twisting (900) < bending sideways (950)
QL Spasm/Trigger Point: clinical characteristrics
–Unlevel pelvis
–Patient’s trunk leans to 1 side
–Very hypertonic muscles on the concave side
–Short leg on side of QL spasm
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
- broad
- Limits extension
anterior cervical fascia
attachements: base of skull, mandible, hyoid, scapula, clavicle, sternum