Exam 3 Flashcards
(36 cards)
rules of medelian genetics
Principle of Segregation
- Genes occur in pairs and only one member of the pair is transmitted to the offspring
Principle of Independent Assortment
- Genes at different loci are
“black urine disease”
Alkaptonuria
Major Types of Genetic diseases
Major Types of Genetic diseases
1: Chromosomal
2: Single gene
- mutation in a single gene
- 95% located in autosomes: dom or recessive
- Follow Mendelian patterns of inheritance
- 5% located in sex chromosomes (X and Y): X or Y linked
3: Multifactorial disorders/complex diseases
* Caused by interactions of multiple genes and the environment
4: Mitochondrial disorders
* Caused by alterations in mitochondrial genome

Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Pattern
- at least 1 affected parent - abnormal phenotype appears every gen
-
affects and can be transmitted by EITHER sex
- Male-to-male transmission can occur and affected males can have unaffected daughters
ONE copy = expression
- 50% child disease is affected x unaffected

Examples of Diseases with Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Pattern (10)
Huntington Disease (HTT)
Familial hypercholesterolemia (LDLR)
HNPCC (MSH2, MLH1,PMS1/2)
Acute Intermittent Porphyria (PBGD)
Postaxial Polydactyly (GLI3)
Achondroplasia (FGFR3)
Marfan syndrome (FBN1)
Osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 (COL1A1/2)
Retinoblastoma (RB1)
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
Huntington Disease
tri-nt repeat (CAG) in chr 4
- signal, txp, protection from apop
- larger number of repeats correlated with earlier age of onset (anticipation)
late-onset neurodegen (35-44 y/o)
- dmg corpus straitum
- chorea (abnorm, invol, writhing mvmt)
- loss motor control
- behav/mood/personality chnages
Penetrance
proportion of individuals carrying a variant (mutation) of a gene that also expresses the associated phenotype
Tendency for greater repeat expansion when disease of _______ origin
paternal

Pedigree of an American Huntington’s Disease Family
Pedigree of family with HD
Individual II-1 is 50 years old, and currently does not manifest any signs of HD.
Question: Do you think II-1 will develop the disease later in life?

yes

Familial Hypercholesterolemia
mutations in LDLR in chr19:
- elevated LDL –> CAD @ young age
- hetero = reduced fxtional LDLRs
most ommon autosomal dominant disorder
- thickened Achilles tendon
- cholesterol deposits in soft tissues:
- xanthelasmas
- xanthomas
- arcus cornealis

HNPCC
“lynch syndrome” - mismatch repair genes
- MSH2 (Chr. 2)
- MLH1 (Chr. 3)
- PMS1 (Chr. 2)
- PMS2 (Chr. 7)
- locus heterogeneity: mutations in different genes –> same phenotype
incr freq of colon/colorectal and endomet ca
Postaxial Polydactyly
Primary genetic defect: Extra fingers or toes
- Mutations in GLI3 gene in Chr. 7
- Ts: patterning of many organs and tissues during development
May exhibit reduced penetrance, variable expressivity
- extra digit may vary from a small skin tag to a fully formed digit

Achondroplasia
FGFR3 gene in Chr. 4:
- txmemb TK receptor that binds fibroblast GF
most cases = NEW MUTATIONS
- less inherited from affected parent: Gly380Arg
bone growth disturbances
- Short limbs relative to trunk length (normal-sized torso)
- Prominent forehead, flattened nasal bridge; and redundant skin folds in arms and legs


mating of 2 pts with achondroplastic dwarfism

Marfan Syndrome
FBM1: chr15
- encodes fibrilin –> affects elastin deposit
mutations:
- missense mutations
- dominate neg effect: mutation fibrillions bind and disable normal fibrillins

FMB1 mutations can also lead to defects in…
ocular: myopia, dispalced lens (ectopic lentis)
skeletal: tall stature, unusually long & slender, scoliosis, hypermobility of joints
CV: MVP, dilatation of ascending aorta
pleiotropism: multiple phenotypic effects of a single gene

Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Pattern:
- affected usual born to unaffected parents (usually asymp - hetero)
- 2 MUTATED copies –> homozygote recessive
- 25% chance of being affected
- increased in indicdence of parental consanguinity
- affects EITHER sex:

proband
affected individual who got genetic testing
Summary: Comparison of Major Characteristics of Autosomal Dominant and Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Patterns

Examples of Diseases with Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Pattern
*CF (CFTR)
*PKU (PAH)
Albinism (TYR)
*Sickle cell anemia
Thalassemia
Alkaptonuria (HGD)
Niemann-Pick Disease (SMPD1)
Tay-Sachs Disease (HEXA)
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP)
Ataxia telangiectasia (ATM)
CF
CFTR: chr7
- delta-F508 is most common mutation
- Cl channel for salt/h20 balance
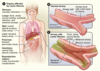
Cystic Fibrosis

if you analyze III-3 and determine that he has the DF508 mutation, what would be the expected PCR product/s for II-4, II-5, III-4, III-5 and III-6?

classic PKU
PAH: chr 12
- complete or almost complete deficiency in enz activity
- most commonly clinc encountered inborn error of aa metab
hypopig if due to lab of tyr
SCREENING for newborns mandatory –> can cause mental-retard
tx:
- limit phe in diet
- supplement with tyr, trp, BCAA (val, leu, ile)








