Final Flashcards
(169 cards)
Principle of Segregation
occur in pairs and only one member of the pair is transmitted to the offspring
Independent Assortment
Genes at different loci are transmitted independently
__% genetic diseases are located on autosomes
95
characteristics
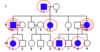
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Pattern
@ least 1 affected parent
can affect either sex
txmit by either sex
child of an affected x unaffected in an auto-dom inherit is __ chnace of being affected
50%
examples of auto-dom inheritance pattern (10)
“dominatrix” - AHH, PORN FAM
Acute Intermittent Porphyria (PBGD)
Huntington Disease (HTT)
Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer (HNPCC, MSH2, MLH1,PMS1/2)
Postaxial Polydactyly (GLI3)
Osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 (COL1A1/2)
Retinoblastoma (RB1)
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
Familial hypercholesterolemia (LDLR)
Achondroplasia (FGFR3)
Marfan syndrome (FBN1)
huntintons
CAG tri-nt repeat in HTT gene in chr 4
- singal, txp, protection from apop
late onset: 35-44 y/o
- dmg corpis striatum
- chorea (abnormal, involuntary writhing mvmts)
- loss of motor control
- behavior/mood/personality changes
penetrance
porportions of individuals carrying variant with associated phenotype
age of onset of huntington’s relationship
largers # repeats = earlier age of onset
Huntington Disease (HD)

Familial Hypercholesterolemia
LDLR in chr 19
- high blood LDL –> high CAD @ young age
- hetero = reduced fx LDLRs
most common auto-dom disorder
- thickened achilles
- choles deposits in soft tissue
- xanthalasma (eye)
- xanthomas (on tendons)
- arcus cornealis (grey spot in iris)

Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer (HNPCC): Lynch Syndrome
mismatch repair: MLH1 (chr 2), MSH2 (chr 3), PMS1 (chr 2), PMS2(chr 7)
- locus heterogeneity
–> incr freq of colon/endomet ca
what is locus hetergeneity
mutations in different genes resulting in same phenotype
Postaxial Polydactyly
GLI3 in chr 7
- Ts in shaping of organs/tissues during dev –> extra fingers and toes
may exhibit:
- reduced penetrance
- variable expressivity (extra digit may be small skin tag to fully formed digit)
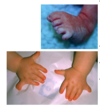
Achondroplasia
FGFR3 in chr 4
- txmemb RTK that binds fibroblast GF
- most cases are due to new mutations
characteristics:
- short limbs with normal torso
- prominent forehead
- flat nasal bridge
- redundant skin folds in arms and legs

Achondroplastic dwarfism

Pedigree of a mating between two
patients with achondroplasia

marfans
FBN1 in chr15: fibrillin in CT (affects elastin deposit)
MANY mutations
- missense = most severe
- dominate negative effect:
- mut fibrillins bind and disable normal
pleiotropism
- multi pheno effects of a single gene
- ocular, skeletal, CV
characteristics
- myopia, ectopia lentis
- tall with long and slender limbs
- joint hypermobility
- MVP, asc aorta dilation

Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Pattern
- affected child born to UNAFFECTED parents
- parents usually carriers but ASYMPTOMATIC
- incr rate in consaguinous parents
- can affect either sex
proband
affected indi
recurrance risk of an auto-recessive diseases for each sibling of proband is…
25%
Examples of Diseases with Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Pattern
TAX CAT NAPS
Tay-Sachs Disease (HEXA)
Ataxia telangiectasia (ATM)
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP)
Cystic fibrosis (CFTR)
Albinism (TYR)
Thalassemia
Niemann-Pick Disease (SMPD1)
Alkaptonuria (HGD)
Phenylketonuria (PAH) - “PKU”
Sickle cell anemia
CF
CFTR in chr 7: delta-F508 is most common
- most common auto-recess disease in caucasians
fx:
- Cl- channel: salt and water balance
- affects lungs, panc

classic PKU
PAH (phenylalanine hydroxylase) in chr 12
- most common inborn error of aa metab
- mousy body odor
char:
- HYPOpig due to lack of tyr
- mental retard (if untx/undx)
tx:
- limit phe and supplement with tyr, trp, and BCAA (leu, ile, val)

incomplete/reduced penetrance
some people with mutation DO NOT show symptoms/phenotype