exam 3 developmental anomalies Flashcards
(32 cards)
Inherited defects (genetic) • Infectious agents (usually viruses) • Nutritional agents (usually deficiencies) • Toxins (often plants or drugs) • Physical agents (rectal palpation, twinning) • Unknown (gestational accidents e.g. anasarca, shistosomus reflexus)
Aetiology
Pathogenesis of Anatomical Developmental Anomalies Occur due to injury of cells during embryogenesis. The nature of the anatomical defect that results depends on:
- timing
- tissue injured
Injury at Zygote Cow 10‐12 days following fertilization results in ?
Death and resorption early returns to breeding / infertility
injury at Embryo (organogenesis) Cow 15‐45 days Ewe 11‐34 days Mare 12‐60 days results in 1 of 2 things
Depends on extent of injury: 1. Developmental anomaly carried to term 2. Death of embryo and abortion
injury at Fetus (growth) Cow 45 days to term Mare 55 days to term Ewe 34 days to term results in?
Illness/ death of foetus resulting in: • Abortion • Mummification • Stillbirths • Weak neonates • Persistent viremia immunotolerance

Palatoschisis (cleft palate/split hard palate) and cheiloschisis (split lip)
Palatoschisis and cheiloschisis is a failure to ___
fuse
Cat oral cavity MDx? Cause

Cat oral cavity MDx: Palatoschisis Etiology: Griseofulvin

polydactyly
Issues?

Pectus excavatum • congenital abnormality of the thoracic skeleton • prominent dorsal deviation of the caudal sternebrae • lateral flaring of the rib cage heart and diaphragm displaced
cat

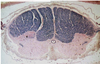
Cat brain MDx: Cerebellar hypoplasia Etiology: Feline panleukopenia virus (parvovirus)
Inherited genes – often autosomal recessive • Spontaneous somatic genetic defect • Chromosomal anomalies • Breed predispositions
what is the difference between communicating and noncommunicating

connecting = choroid plexus makes CSF opened to the sub aratenoid layer and expand the skull
Name the anomalies associated with the persian cat

• polycystic kidney disorder (PKD) • cardiomyopathy • cataracts • cleft palates & cleft lips • mega‐oesophagus • portosystemic shunt (liver) • patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) • entropion • amyloidosis • mucopolysaccharidosis
These are cysts in can kidney Mdx?
cause?

Cat kidneys MDx: Renal cysts Disease: Polycystic kidney disease Etiology: Inherited genetic defect
Name the cat

Congenital Defects ‐ Genetic Manx cat: 17% of kittens show genetic malformations & high mortality due to spinal defects
dog pancreas Type of anatomical defect: failure to develop

MDx: pancreatic aplasia Disease name: Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
What type of anatomical defect?

failure to form
Abnormal development of a structure can lead to hip displasia what are some of the anatomical defects that can lead to this


whats the defect

Arthrogryposis
Whats the defect (Mdx)

Hydranencephaly
Calf spinal cord in —— gestation MDx: Severe nonsuppurative myelitis
early

lamb buttless butt

MDx: atresia ani
What is the MDx and one what day does this toxic symptom result in this baby

MDx: Synophthalmia Etiology: Veratrum californicum day 14 gestation Cyclopamine toxin from plant









