Exam 3 Lecture 1 Flashcards
(35 cards)
define competition:
direct interaction
interaction between organisms, populations, or species, in which birth, growth and death depend on gaining a share of a limited environmental resource.

define predation:
direct interaction:
negative or positive interaction between two species, including competition, predation, herbivory, and mutualism, that occurs without the involvement of an intermediary species.

define herbivory:
direct interaction
negative or positive interaction between two species, including competition, predation, herbivory, and mutualism, that occurs without the involvement of an intermediary species.

define parasitism:
realized niche the actual niche of a species whose distribution is restricted by biotic interactions such as competition, predation, disease, and parasitism

define Commensalism:
an interaction between two species in which one species is benefited and the other is neither benefited nor harmed.

define indirect commensalism
an interaction in which one species benefits another species indirectly, through an intermediary species, without itself being helped or harmed.
define Amensalism:
any relationship between organisms of different species in which one organism is inhibited or destroyed while the other organism remains unaffected.

define Mutualism:
interactions between individuals of different species that benefit both partners. (

What’s this?

Nectar Robbing
Parasitism

What isn’t a bee and nectar robs?
shit-nosed hummingbirds

Even though the bird doesn’t eat the bush it still affects the bush _____
name the relationship

Mutualism


The water lily absorbs sunlight before anything beneath it can.
That’s exploitation competiton

_________can influence population distribution and abundance
Intraspecific
competition

This example was ____

Exploitation competiton
(direct)
Intraspecific competion through direct interaction between individuals

Example: Absorbing Sunlight

In exploitation competition
organisms use up resources directly. Once used, the resource is no longer available for other species to use.
In interference competition,
one organism prevents other organisms from using the resource. Interference competition can occur, particularly where the resource is “patchy” - only occurring in discrete patches - and thus able to be defended.
Define Self-thinning
The progressive decline in density which accompanies and interacts with the increasing size of individuals in a population of growing individuals.

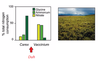
What do these data model?


What does N/K also represent?


What Suggests that more than one species cannot occupy the same niche?
Competative Exclusion Principle!

What is the result of overlapping niches
Competitive Exclusion

Competitive exclusion principle
Differences in the _________ of different species
cause their…..
competitive ability,
abundances to diverge over time

Competitive exclusion principle
One species _____________while the other_________
becomes more common,
becomes less common –> excluded