EXAM 4 Adaptive Immune Disease Flashcards
(34 cards)
autoimmune diseases are loss of ___, leading to ___ reactions
- tolerance
- hypersensitivity
describe autoimmune diseases
- adaptive immune targeting of self
- humoral or cell mediated
- often chronic and life long
- loss of self-tolerance
- hypersensitivity reactions - type II, III, and IV
what are mechanisms that contribute to immunological self-tolerance?
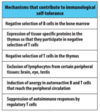
autoimmune disorders are caused by ___, ___, or ___
genetics, the environment, or both
there are more than ___ autoimmune diseases
80
___% of the US population is affected by autoimmune disorders
3%
autoimmune diseases are among the 10 leading causes of death among what population?
women under 65
genetic predisposition to autoimmune diseases is important. only ___% of predisposed individuals get autoimmune disease
20%
are there infectious and non-infectious causes of autoimmune diseases?
yes, both
___ subtype influences autoimmune disease development
HLA
how do HLA subtypes influence autoimmune disease development?
- HLA genes associated with susceptibility in 50% of autoimmune diseases
- class II alleles most frequently implicated
- CD4 T cells closely tied to autoimmune disease development
- susceptibility does not always lead to disease
type II hypersensitivity is mediated by what immunolobulins?
IgG or IgM
type II hypersensitivity reactions target ___
cell surface proteins
in type II hypersensitivity, are antibodies agonistic or antagonist?
they can be both
rheumatic fever is caused by ___
molecular mimicry
describe the pathogenesis of rheumatic fever
- staph pyogenes throat infection
- s. pyogenes cell wall shares human epitopes
- transient due to lack of T cell help
- demonstrates T cell necessity for prolonged autoimmunity

describe graves disease
- antibody binding causes metabolic dysfunction
- antibodies function as a TSH agonist
- CD4 Th2 response
- excessive thyroid hormone release
- antibodies do not cause overt tissue damage
- hyperthyroid condition - weight loss, heat intolerance, anxiety and irritability, exophthalmos
- thyroid ablatement

describe how antibody-mediated autoimmune disorders can be temporarily transferred to newborns

what is hashimotos disease?
- destruction of normal thyroid tissue
- CD4 Th1 response
- hypothyroidism
- ectopic lymphoid tissue formed in the thyroid
- enlarged thyroid present swallowing difficulty
___ is a form of hypothyroidism, and ___ is a form of hyperthyroidism
- hashimotos disease
- graves disease
___ is a disease that causes progressive destruction of the exocrine glands
sjogrens syndrome
describe how sjogrens syndrome is one of the most common autoimmune disorders
- 0.5% to 5% prevalence
- 9 times more prevalent in women
- utah has one of the largest known patient populations
sjogrens syndrome is a type ___ hypersensitivity
II
what are some clinical manifestations of sjorgrens syndrome?
- dry eyes, dry mouth, and arthritis
- dramatically reduced salivary flow, tongue scaling, diffuse submandibular swelling, prominent caries, oral candidiasis




