Femal reproductive system and breast Flashcards
(71 cards)
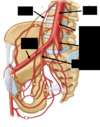
What parts of the female reproductive tract are in the pelvic cavity?
Ovaries
Uterine tubes
Uterus
Superior vagina
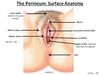
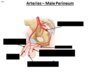
What parts of the female reproductive tract are in the perineum?
inferior vagina
Perineal muscles
Bartholin’s glands
Clitrois
Labia
What is the pouch between the utereus and and the bladder
uterus and rectum
Vesico uterine pouch
recto-uterine pouch
What do you put a needle through to drain the pouch of douglas?
posterior fornix of the vagnia
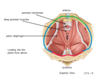
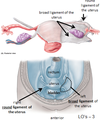
Where is the broad ligament

What is the broad ligament made up of?
Double layer of peritoneum
What is the function of the broad ligament?
Maintains uterus in the midline
What is contained within the broad ligament?
Uterine tubes
Proximal round ligament
What does the round ligament attatch to?
Lateral aspect of uterus
through deep inguinal ring
superficial tissue of the female perineum
Where is the round ligament?
What supports the utereus in place?
Uterosacral ligaemnts
Endopelvic fascia
Levator ani
What are the 3 layers of the uterus body?
Perimetrium
Mymometrium
Endometrium
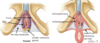
What are the two ways the utereus can sit?
What does this mean?
what is more common?
Anteverted anteflexed (flopped over bladder)
Retroverted retroflexed ( flopped over colon)
vertered means cervix and flexed means utereus
anteverted anteflexed is most common
Where does fetilisation usually occour?
Ampulla
What are the parts of the fallopian tube

What do you call the space in the vagina around the cervix?
Fornix
What forms the majority of the pelvic diaphram?
Levator Ani
What nerve supplies the levator ani and where does it come from?
nerve to the levator ani
S3,S4,S5 sacral plexus
what nerve supplies the perineal muscles?
Pudendeal nerve
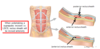
What is the perineal body?
bundle of collangenous elastic tissue which the perineal muscles attatch too
What do you call the little anchor point the perineal muscles attatch too?
The perineal body
Where are the bartholins glands?
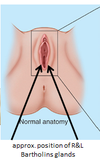
what is the area anterior to the pubic bone?
mons pubis
Label dans la vaginous