Fertilisation & blastocyst development phys. Flashcards
(31 cards)
Define ‘ontogenetic development’
Development of an individual to maturity
What are the 2 stages ontogenetic development is split into?
- Prenatal stage - begins with fertilisation off egg, ends at birth
- Post-natal stage - begins at birth, ends when animal sexually mature
What are the stages of the pre-natal stage?
- Fertilisation
- Cleavage
- Gastrulation
- Organogenesis
- Foetal growth & cell differentiation
- Gametogenesis
What occurs during fertilisation?
- Cumulus cells surrounding zona pellucida expand, substance between cells becomes gel like
- Sperm penetrate this layer, bind to zona via ZP3 protein
- Once fused, acrosomal reaction takes place causing deterioration of sperm outermembrane, laying bare inner membrane. Proteolytic enzymes are released
- Inner membrane contains receptor for ZP2 protein
- Proteolytic enzymes break down zona, sperm binds to ZP2
- Zona breaks down, sperm & egg membranes fuse
- Sperm nucleus enters egg cytoplasm, fertilisatin occurs
- Entry of nucleus triggers Ca wave within egg
- Cortical granule reaction occurs, hardening zona pellucida preventing more than 1 sperm fertilising the egg
- Egg completes 2nd mitotic division
- Sperm nucleus decondenses, female & male pronuclei develop - 1st cleavage division
When does the 1st mitotic division occur?
20-24hrs after fertilisation
Define ‘embryo cleavage’
The development of the single fertilised cell into a multicellular complex within the zona pellucida
Describe what happens during embryo cleavage
- Zygote undergoes mitotic divisions to form blastomeres which are totipotent
- Cell gets progressively smaller
- After 3-4 divisions are 8-16 cells, blastomere becomes morula
- Morula enters uterus at day 4
Draw a table to illustrate the different stages of embryo cleavage including no. of cells, stage and time after fertilisation
* once enters morula stage cells are pluripotent

Describe development from a morula to blastocyst
- Blastomeres become compressed against each other, form tight junctional complexes with adjacent cells
- Morula draws in uterine fluid until embryo has central fluid filled cavity with a clump of cells pressed against one pole
- Occurs from 5 days after fertilisation
- Is now blastocyst
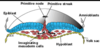
Describe the structure of a blastocyst
- Trophectoderm - ectoderm like epithelium
- Inner cell mass (ICM) - clump of pluripotent cells at one pole
- Blastocoele - fluid filled space within blastocyst

How can twins be formed?
- Dizygotic - arise from 2 seperate ova, each fertilised by a seperate sperm
- Monozygotic - arise from a single ova fertilised by a single sperm which splits at the blastomere stage/duplication of ICM within blastocyst
Describe what occurs during implantation
- Blastocyst grows in size until zona breaks
- Trophoblast cells contact maternal tissue, initiates implantation for nutrition
- Trophoblast provides signals for maternal recognition of pregnancy
- ICM proliferate to form embryonic disc
What occurs during expansion of the blastocyst?
- Ruminants and pigs
* after hatching from zona blastocytes expand enormously in 2nd week (upto 1cm/hr in pigs)- Mares
- hatch but are covered in glycoprotein capsule that remains spherical
- Mares
How early can pregnancy be detected in the mare?
14 days after ovulation due to embyronic vesicle. Appears black on ultrasound.
Describe what happens during gastrulation
- Rearrangement of ICM cells by morphometric movement to form 3 germ layers of embryo
- First formation is of bilaminar embryo
- Second formation is of trilaminar embryo
What makes up the bilaminar embryo?
- Outer trophoblast cells covering ICM degenerate
- ICM cells exposed and proliferate to form embryonic disc
- Hypoblast layer forms on underside of ICM as a continuous sheet lining the interior of blastocyst
- Emrbyonic disc made up of 2 layers; epiblast & hypoblast
- Extra-embryonic endoderm surrounds blastocoele forming yolk sac

Define gastrulation
The rearrangement of the 2 layers (epiblast/hypoblast) & proliferation with morphic movements to form 3 germ layers that are intra-emrbyonic
What are the 3 germ layers formed by gastrulation?
- Ectoderm (outer) - becomes epithelial (skin) & neural tissue
- Mesoderm (middle) - becomes muscle, bone, blood, heart & connective tissue
- Endoderm (inner) - becomes gut lining & associated structures (organs)
Define the ‘primitive streak’
- Thickening caused by epiblast cells that migrate & proliferate along the diameter of the embryonic disc causing elongation
- Forms 2 ridges with a depression in the centre called the primitive groove
- Epiblast cells migrate down the primitive groove to the cranial end and form a mound of cells known as the primitive knot/Henson’s node
What are the functions of the primitive streak and primitive node?
- Streak - form mesoderm
- Node - form notochord (neuroectoderm) and mesoderm of the head
What happens during formation of mesoderm?
- epiblast cells proliferate & migrate into the primitive streak
- starting caudally, cells migrate ventrally through the groove
- forms a loose arrangement of cells between the epiblast & hypoblast called the mesoderm
- these layers expand laterally to form the trilaminar embryo - NOT into buccopharyngeal plate or cloacal membrane
- epiblast becomes ectoderm, hypoblast becomes endoderm
Where does the notocchord form?
- in front of the primitive streak
- expands cranially as a solid rod of mesoderm
- marks the cranio-caudal axis of embryo
- underlies & induces differentiation of future nervous system

What leads to differentiation of the neural ectderm?
The fact that the embryonic disc grows much faster than the primitive streak
What are the 3 derivatives of the mesoderm?
- Paraxial mesoderm - develops into skeleton, muscles
- Intermediate mesoderm - develops into urogential tract
- Lateral mesoderm - immediately splits into 2 cell layers




