Final 2013 Flashcards
(194 cards)
The picture represents which mechanism?
a. Cooperativity
b. Potentiation
c. Summation
d. Synergism

a. Cooperativity
What is the diagnosis according to the ECG shown?
a. Anterior STEMI (ST elevation in V2-V4)
b. Angina pectoralis
c. Pericarditis
d. Inferior STEMI

a. Anterior STEMI (ST elevation in V2-V4)
What does the figure represent?
a. aortic insufficiency
b. mitral stenosis
c. Severe LV dysfunction, often in advanced aortic stenosis
d. Bigeminal pulse
e. Cardiac tamponade
f. Heart failure

a. aortic insufficiency
What does the figure represent? a. aortic insufficiency b. mitral stenosis c. Severe LV dysfunction, often in advanced aortic stenosis d. Bigeminal pulse e. Cardiac tamponade f. Heart failure
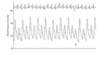
c. Severe LV dysfunction, often in advanced aortic stenosis
EBM question had a description of a study with similar table

-
What is associated with an immediate acute blood transfusion reaction?
a. IgE
b. IgG
c. IgM
d. IgA
c. IgM
A patient came with fatigue & fever, CBC showed high WBCs, & blood smear shower Auer rods. What is the diagnosis?
a. AML
b. CML
c. ALL
d. CLL
a. AML
A Rhesus factor positive test refers to the presence of which antigen on the RBCs?
a. A antigen
b. B antigen
c. O antigen
d. D antigen
e. AB antigen
d. D antigen
What results in type 2 hypersensitivity reaction following blood transfusion?
- Antibodies adsorbed on RBC membrane
- Immune complex deposition
- Cytokines releas
- Antibodies adsorbed on RBC membrane
What is the main enzyme for fibrinolytic action?
- Thrombin
- Plasmin
- Fibrinogen
- Plasmin
A patient with a history of recurrent infections presented with fever & sore throat, what would you find in his blood smear?
a. Eosinophilia
b. Basophilia
c. Leukocytosis
d. Thrombocytosis
c. Leukocytosis
Which of the following acts as a substrate for plasmin & thrombin?
a. Fibrinogen
b. Plasmin
c. Factor Xlll
d. Factor V
a. Fibrinogen
What serves as the main hematopoietic organ in the 8th month of gestation of a fetus? Lymph nodes Spleen Bone marrow Yolk sac Placenta
Bone marrow (Hematopoiesis starts in the spleen during the 3rd month, peaks in the 5th, and ceases by the 7th)
What is not a characteristic with extravascular hemolysis?
High bilirubin
Decreased haptoglobin
Splenomegaly
Reticulocytopenia
Decreased haptoglobin (I understand the note has this in the table but all others are absolutely wrong and this is not a characteristic)
Drug that bind to G11b/111a receptors and inhibits their activation?
a. Otamixaban
b. Abciximab
c. Aspirin
d. Clopedogril
e. Rituximab
b. Abciximab
Drug that do not have an antidote in case of bleeding?
a. Otamixaban
b. Abciximab
c. Aspirin
d. Clopedogril
e. Rituximab
a. Otamixaban
Patient presented with macrocytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and hypo-segmented neutrophils.
a. Megaloblastic Anemia
b. MDS
c. IDA
d. Aplastic anemia
b. MDS
Which drug is a direct inhibitor of thrombin?
a. Dabigatran
b. Aspirin
c. Heparin
d. Warfarin
a. Dabigatran
which phospholipid is exposed on the surface of damaged RBCs
a. Phosphatidylserine
b. Phosphatidylcholine
a. Phosphatidylserine
Which drug cause hemorrhagic cystitis as a side-effect?
Cyclophosphomide
Doxarubicin
Cisplatin
Methotrexate
Cyclophosphomide
What is the mechanism of action of Doxarubicin as a cytotoxic antibody?
Depletes cell metabolites
Intercalates RNA and DNA
Prevents cell membrane synthesis
Mitotic poison
Intercalates RNA and DNA
A patient admitted for infection with high PT, APTT, & D-dimers. What is the cause?
DIC
Hemolytic anemia Hemophilia C
DIC
What is the mechanism of action of deferoxamine?
Cross links DNA
Binds to iron and enhances its excretion
Regulate DNA expression
It has an unknown mechanism of action
Binds to iron and enhances its excretion
How do phagocytes help in anti-bacterial defense?
a. Release of cytokines
b. Release of reactive oxygen species
c. Release of histamine
b. Release of reactive oxygen species


