Final Exam - Eye Histology Flashcards
(112 cards)
The eyeball is located in the skull’s bony socket called the ___________.
orbit
List the accessory ocular structures, also known as the ADNEXA
- Palpebrae (eyelids)
- Third eyelid and conjuctiva
- Lacrimal apparatus
If you’re buying accessories from woman, you have to remember to _P_ay _T_he _L_ady
The eye is composed of:
1 lens and 3 tunics (fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, retina)
The fibrous tunic of the eye is composed of:
- Sclera
- Cornea
- Limbus
The fibrous layer is that _S_tupid _C_orneal _L_ayer

The vascular tunic of the eye is composed of:
- Iridocorneal angle
- Iris
- Ciliary body
- Choroid
The vascular tunic _I_s _I_n _C_hris’s _C_ranium

What is the neuro-epithelial tunic composed of?
the retina

What are the functions of the sclera?
- protects the eye
- maintains the shape of the eye
- provides insertion points for tendons of extraocular muscles

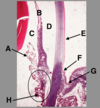
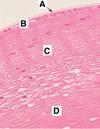
Identify the area of the eye indicated by the box.

The cornea
The cornea is the anterior portion of the eye. This is an avascular, transparent convexconcave lens.
The _________ is the anterior portion of the eye. This is an avascular, transparent convexconcave lens
The cornea is the anterior portion of the eye. This is an avascular, transparent convexconcave lens
The cornea is comprised of ___ layers? (how many)
Name the layers!
The cornea is comprised of 5 layers.
- anterior corneal epithelium
- anterior limiting lamina/subepithelial basement membrane, supporting the lining epithelium
- Substantia propria - stroma of cornea
- Posterior limiting lamina/membrane - Descemet’s membrane, supporting the epithelium
- Posterior epithelium of cornea - corneal endothelium
5** _A_ssholes _A_re _S_elling _P_arty **Pills in the corn(ea)** **field
Identify ‘1’ in this H&E section of the cornea.
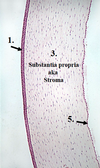
anterior corneal epithelium
Identify ‘5’ in this H&E section of the cornea.

Posterior epithlieum of the cornea
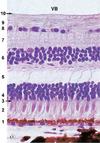
Identify ‘1’ in this H&E section of a rat cornea.

Anterior corneal epithelium
Identify ‘2’ in this H&E section of a rat cornea.

Anterior limiting membrane
Identify ‘3’ in this H&E section of a rat cornea.

Stroma (substantia propria)
Identify ‘4’ in this H&E section of a rat cornea.

Descemet’s membrane
Identify ‘5’ in this H&E section of a rat cornea.

Posterior epithelium (corneal endothelium)
__________ is the corneoscleral junction where the opaque sclera overlaps the transparent cornea. This area has small blood vessels.
Limbus is the corneoscleral junction where the opaque sclera overlaps the transparent cornea. This area has small blood vessels.

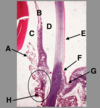
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow.
Which tunic is this found in?

Limbus, found in the fibrous tunic.
inflammation of structures in the uvea (the vascular tunic of the eye) is known as ___________.
Uveitis
In the vascular tunic (uvea), the ________ is located anterior to the lens and separates the anterior and posterior chambers.
In the vascular tunic (uvea), the iris is located anterior to the lens and separates the anterior and posterior chambers.
In the vascular tunic (uvea), the ________ suspends the lens, contains smooth muscle for accommodation; has processes covered by secretory epithelium.
In the vascular tunic (uvea), the ciliary body suspends the lens, contains smooth muscle for accommodation; has processes covered by secretory epithelium.
In the vascular tunic (uvea), the ________ is the vascular supply to the optical retina. Contains pigment.
In the vascular tunic (uvea), the choroid is the vascular supply to the optical retina. Contains pigment.
The _______ is the region where the transparent cornea merges with the vascular sclera
The limbus is the region where the transparent cornea merges with the vascular sclera