Final Exam [INCOMPLETE] Flashcards
(260 cards)
1
Q

A
Supraoccipital Bone
2
Q

A
Parietal Bone
3
Q

A
Frontal Bone
4
Q

A
Exoccipital Bone
5
Q

A
Nasal bone
6
Q

A
Premaxillary Bone
7
Q

A
Maxillary Bone
8
Q

A
Lacrimal Bone
9
Q

A
Jugal Bone
10
Q

A
Quadratojugal Bone
11
Q

A
Supraoccipital Bone
12
Q

A
Lacrimal Bone
13
Q

A
Parietal Bone
14
Q

A
Premaxillary Bone
15
Q

A
Frontal Bone
16
Q

A
Nasal Bone
17
Q

A
Maxillary Bone
18
Q

A
Jugal Bone
19
Q

A
Quadrate Bone
20
Q

A
Interorbital Septum
21
Q

A
Basioccipital Bone
22
Q

A
Basisphenoid Bone
23
Q

A
Palatine Bone
24
Q

A
Squamosal Bone
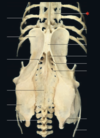
25
The Articular Surface for the Mandible is found on the...
Articular Bone
26
4
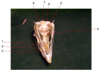
Pterygoid Bone
27

Urohyale
28

Paraglossum
29

Epihyale
30

Ceratohyale
31

Basihyale
32
What is shown?

The Hyobranchial Apparatus
33
Notarium
34

Unicate Process
35

Synsacrum
36

Pygostyl
37

Sternum
38

Sternal Rostrum
39

Craniolateral Process
40

Lateral Trabecula / Thoracic Process
41

Median Trabecule
42

Carina
43

Intermediate Trabecule / Abdominal Process
44

Clavicle / Furcula
45

Scapula
46

Coracoid Bone
47

Triosseal Canal
48

Humerus
49

Ulna
50

Radius
51

Radial Carpal Bone
52

Ulnar Carpal Bone
53

Carpometacarpus
54

*Ossa Digitorum Manus*
55

Renal Fossa
56

Preacetabular Wing of the Ilium
57

Postacetabular Wing of Ilium
58

Wing of Ischium
59

Ilioischiadic Foramen
60

Ischiopubic Window
61

Obturator Foramen
62

Acetabulum, Acetabular Foramen, Antitrochanter
63

Patella
64

Ossa Digitorum Pedis
65

Tarsometatarus
66

Fibula
67

Tibiotarsus
68

Femur
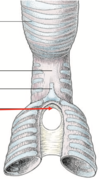
69
Number of Vertebrae in the Bird
Cervical: 13
Thoracic: 7
Lumbar + Sacral: 14
Coccygeal: 7
70

Pectoralis Muscle
*Downstroke Muscle*
71

Supracoracoideus Muscle
## Footnote
* Upstroke Muscle*
* Passes through the canalis triosseus*
72
Muscle used in the flexion mechanism of the digits when perching
*m. ambiens*
73

Gall Bladder
74

Spleen
75

Cloaca
76

Large Intestine
77

Gizzard / Ventriculus
78

Proventriculus
79

Crop
80

Oesophagus
81

Small Intestine
82

Double Caecum
83

Duodenal Loop / Duodenum
84

Pancreas
85

Liver
86
What are the three functions of the Crop?

Store Food
Moisten food
Sometimes Produce Crop Milk
87
What is the function of the Gizzard / Ventriculus?
Mechanical Digestion
## Footnote
*Contains small stones*
88

Infundibular Cleft
89

*Aditus laryngis*
Laryngeal Inlet
90

Lingual Papillae
91

Pharyngeal Papillae
92

Palatine Ridge / Palatine Papillae
93

Choana
94
Tongues **without** intrinsic muscles are...
**non**-protrudable
## Footnote
*Intrinsic muscles are needed in order for the tongue to protrude*
95
The crop is absent in...
Ducks, Geese, Owls
96
Crops are usually observed in...
Seed eating birds
97
Pigeons posess prolactin-sensitive epithelial cells in their crops which allow...
Production of crop-milk for chicks
98
The Hepatic peritoneal cavities are bound by the...
Posthepatic Septum
99
A

Stomach, Ventral Surface
100
B

Stomach, Opened Ventrally
101
1

Oesophagus
102
2

Proventriculus
## Footnote
*ventriculus glandularis*
103
3

Papillae
104
4

Deep Proventricular Glands
105
5

Lumen of Gizzard
106
6

Caudal Blind Sac
107
7

Cranial Blind Sac
108
8

Pyloric Orifice
109
9

Cranioventral Muscle Mass
110
10

Duodenum
111

Proventriculus and Ventriculus
112

*M. crassus cranioventralis*
containing saccus cranialis
113

*M. crassus caudodorsalis*
containing saccus caudalis
114

Ventriculus
115

Gastric Isthmus
116

Proventriculus
117

Descending Duodenum
118
Name the Yellow area

Cuticle
## Footnote
*cuticula gastris*
119

Descending Duodenum
120

Cloaca
121

Colorectum
122

Jejunum
123

Meckel's Diverticulum
## Footnote
*yolk duct remnant*
124
Which ducts enter the Ascending Duodenum?
* Ductus pancreaticus*
* Ductus coledochus*
125

Ileum
126

Urodeum
127

Ductus Deferens
128

Ureter
129

Phallus
130

Vent
131

Coprodeum
132

Coprourodeal Fold
133

Cloacal Bursa
134

Proctodeum
135

Rectum
136

Caudal Mesenteric Artery
137

Caudal Renal Vein
138

Caudal Renal Portal Vein
139

External Iliac Vein
140

Common Iliac Vein
141

Caudal Renal Vein
142

Cranial Renal Vein
143

Cranial Renal Portal Vein
144

Ischiadic Vein
145

Afferent Veins
146

Caudal Mesenteric Vein
147

Interiliac Anastomosis
148

Internal Iliac Vein
149

Median Sacral Artery
150

Descending Aorta
151

Internal Iliac Artery
152

Caudal Renal Artery
153

Ischiadic Foramen
154

Ischiadic Artery
155

Middle Renal Artery
156

External Iliac Artery
157

Efferent Veins
158

Coeliac Artery
159

Cranial Mesenteric Artery
160

Cranial Renal Artery
161

Caudal Vena Cava
162

Renal Portal Valve
163
What is shown?

Proximal Larynx
164

Arythenoid Cartilage
165

Cricoid Cartilage
166

Precricoid Cartilage
167

Trachea Cartilage
## Footnote
*fully circular, unlike most mammals*
168

Abdominal Air Sac
## Footnote
*paired*
169

Caudal Thoracic Air Sac
170

Cranial Thoracic Air Sac
171

Lung
172

Clavicular Air Sac
## Footnote
*L & R sacs are fused*
173

Cervical Air Sac
174
Describe the blood flow furing rest
Blood passes **caudally** through **afferent veins** to the **kidney**
175

Left Brachiocephalic Trunk
176

Right Brachiocephalic Trunk
177

Right Common Carotid Artery
178

Right Cranial Vena Cava
179

Right Atrium
180

Left Subclavian Vein
181

Left Cranial Vena Cava
182
How many cups are found on the right Atrioventricular valve?
1
183
How many cusps are found on the left Atrioventricular valve?
3
184
Where most animals have intercostal arteries, birds have...
Intersegmental Arteries
185

Trachea
186

Syrinx
187

Lung
188

Heart
189
What is shown?

The syrinx
190

Pessulus
191
Interbronchial Ligament
192

Sternotracheal Muscle
193
Which structure is found between the tympanum to the bronchial cartilages?
Lateral Tympaniform Membrane
194
When primary bronchi enter the lung, they are known as...
Mesobronchi
195

Lateral/Medial Tympaniform Membrane
196

Clavicular Air Sac
197
Muscle found along the trachea
Lateral tracheal muscle
198
Which regions of the lung are regarded as 'neopulmo'?
Lateral Dorsal Sector
199
Which regions of the lung are regarded as 'paleopulmo'?
Mediodorsal sector
Medioventral sector
Lateroventral sector
200
What is shown?

Parabronchi
201
With the exeption of the abdominal air sacs, air travels to the air sacs via the...
Secondary Bronchi
202
Which location can fluid be removed and vaccinations be put into a bird?
Infraorbital Sinus
203

Caudal Nasal Concha
204

Rostral Nasal Concha
205

Middle Nasal Concha
206

Middle Renal Division
207

Caudal Renal Division
208

Cranial Renal Division
209
What is the non-protrusible phallus composed of?
Median Phalic Body (Unpaired)
Lateral Phalic Bodies (Paired)
Lymphatic Bodies
210

Gelatinous Body
211
Which nerve is found between the middle and caudal liver sector?
Isciadic Nerve
212

Calamus
213

Proximal Umbilicus
214

Vexillum
215

Rachis
216

Umbilical Barbs
217

Distal Umbilicus
218
The rachis and the calamus form the...
Scapus (Core)
219

Down Feather
220
Give the two types of contour feather
Remiges
Retricies
221
Remiges are...
'Rowing feathers'
222
Retricies are...
'Steering feathers'
## Footnote
*tail feathers*
223
What kind of feather is found on the head of a bird?
Hair Feathers
224
Which bones is the Furcula made of?
2 clavicular bones
225
Canalis triosseus is composed of...
Furcula
Os Coracoideus
Scapula
226
Which muscle passes through the canalis triosseus?
*m. supracoracoideus*
227
A furcula is needed in order to...
Fly
228
Can air sacs pass thorugh bones?
Yes
229
True or false, birds have two rows of carpal bone
True
230
True or false: the tarsometatarsal is made of tarsal and metatarsal
False
231
Sinus infraorbitalis is in contact with...
Concha nasalis caudalis
232
The proximal Larynx is composed of...
Cricoid Cartilage
Precricoid Cartilage
Arythenoid Cartilage (Paired)
233
What is the Pessulus?
Connects the tympanic cartilage
First point of bronchial cartilages in the syrinx
234
Which muscle is used in vocalisation of the birds?
m. sternotrachealis
m. trachealis lateralis
235
Give the muscles of the stomach
m. crassus cranioventralis
m. crassus caudodorsalis
236
How many liver lobes do birds have?
2
237
How many gall bladders do birds have?
1
238
How many pancreatic lobes do birds have?
3
239
The aorta of the bird is located on the...
Right
240
Long-flying feathers are called
Anulles?
241
Ventral Side feathers are called
Down Fearthers
242
If the Caudal Renal Portal Vein is closed, blood travels...
Back into the portal system
243
True or false, the portal system is open when the bird is resting
True
244
Is the portal of the kidney seen in non flying birds and flying birds?
Yes
245
Which nerve is found along with the Optic Chiasma?
n. trachialis
246
Name of the dorsal spinal cord
Corpus gelatinosum
247
Which muscle opens the larynx?
m. dilatatom glottitis
248
Which muscle closes the larynx?
m. constrictor glottis
249

Furcula
250

*Os coracoideum*
251

Scapula
252
What is the function of the supracoracoideus muscle?
Stabilise the wing
253
How many crops do pigeons/doves posess?
2
254
What is fissure of the brain is characteristic in birds?
Fissura Longitudinale
255
What kind of valves can be found in the left atrioventricular opening of the bird's heart?
3 Cusps
| (Tricuspid Valve)
256
Where can you find exactly the *corpus gelatinosum*?
Between the left and right **dorsal funiculi** of the **lumbosacral spine**
257

*divisio renalis media*
258
The renal portal valve is...during rest
Closed
259
Can renal portal circulation be found in non-flying birds?
Yes
260

Central Tendon


