Final Review Flashcards
(219 cards)
What are the common disc protrusion sites?
T12-T13, T13-L1, C2-C3, C3-C4
Why is anesthesia recommended for spinal radiographs?
Prevents narrowing of the disc space with muscle spasms
In spinal radiographs, high ___ and low ___ create better contrast
high kVp, low mAs
Use of a ____ increases contrast for spinal radiographs
Grid
When positioning for a spinal radiograph, the vertebral column must always be _____ with the table top
parallel
When positioning for spinal radiographs, the disc spaces must be _____ with the table top
perpendicular
Common views for spinal radiographs
lateral and VD
Use of smaller cassettes and multiple views for spinal radiographs allow for what?
Perpendicular view of the disc spaces
Why are DV spinal views not as accurate?
Not parallel
Object-film distance distortion
How many views may be required for a full spinal study on a dog vs a cat?
Dog - 4-5 views
Cat - 1-2 views
What is the vertebral formula?
C7 T13 L7 S3 Cd20+ (tail)
Vertebral bone with no spinous process and two large lateral wings, articulate via synovial joints allowing greater movement
Atlas (C1)
Vertebral bone with large “blad-like” spinous process, peglike dense at cranial aspect forming atlantoaxial joint. No intervertebral disc between C1 and C2, articulates caudally with C3 via intervertebral disc
Axis (C2)
Vertebral bone with large transverse process (ventral lamina)
C6
What species has 18 pairs of ribs? (One breed does not)
Horses
Species with thoracic vertebrae that have tall spinous processes, large articular facets that form joints with the heads of the ribs
Dogs
In what species are rib heads cranial to respective vertebral body?
Cat
Where would you find the narrowest intervertebral disc space in a dog?
Between T10-T11
Which vertebra is the Anticlinal vertebra?
T11
What species have 4 fused vertebrae making up the sacrum?
pigs and sheep
What species have 5 fused vertebrae making up the sacrum?
Horses, cattle, goats and humans
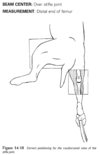
Where should the beam be centered for a lateral view of the cervical spine?
C4
Where should the measurement be taken for a lateral view of the cervical spine?
C6
What should be included in the field of view for cervical spine XRays?
Base of skull to first few thoracic vertebrae