FUN4/Lipids Flashcards
(72 cards)
a fatty acid is a _____ _____ chain with a terminal ____ group
hydrophobic, hydrocarbon, carboxyl
2 types of fatty acids
unsaturated and saturated
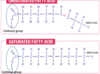
A __________ means that the two hydrogen atoms adjacent to the double bond stick out on the same side of the chain.
cis configuration

eicosanoids are poly__________ FAs with ____ carbons
unsaturated, 20
prostaglandins (PG) are synthesized from _____ acid via _____
arachidonic, cyclooxygenase(COX)
PG’s are _____, but have a short half life,
potent/strong
half life of PGs
seconds
what are the roles of PGs
inflammatory, platelet homeostasis
PG’s are _______ FAs
signalling
Leukotrienes are _____ FAs
signalling
leukotrienes are part of the _____ family
eicosanoid
Leukotrienes are synthesized from ______ acid via ______
arachidonic, lipoxygenase (LOX)
leukotrienes have a (longer/shorter) half life than prostaglandins
longer
half life of leukotrienes
4 hours
what are the roles of leukotrienes
inflammatory, neutrophil adhesion
4 classifications of lipids
FAs and their derivatives, lipids with glycerol, lipids without glycerol, lipoproteins and lipopolysaccharides
2 types of fatty acids
prostaglandins and leukotrienes
what are the lipids containing glycerol

what are lipids that dont contain glycerol
steroids and sphingolipids
3 main functions of lipids
energy, strucutre, cellular signaling
which lipids are involved in cellular signaling events
steroids, prostaglandins, leukotrienes
triglycerides are the ____ in our bodies
fats
a triglyceride is made up of ______
a glycerol and 3 fatty acids
what type of tissue are triglycerides stored in
adipose tissue

















