Fundamentals Flashcards
(76 cards)
What is the volume of the bony orbit?
Approximately 30cm
What is the average height and width of the orbital entrance?
35mm in height 45mm in width
Where is the maximum width of the orbit?
Approximately 1 cm behind the anterior orbital margin.
What is the average depth of the orbit?
From 40 to 45 mm from the orbital entrance to the apex
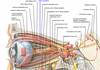
What are the seven bones that make up the bony orbit?
- Frontal bone
- Zygomatic bone
- Maxilla (or maxillary bone)
- Ethmoid (or ethmoidal bone)
- Sphenoid bone
- Lacrimal bone
- Palatine bone
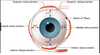
What bones make up the orbital margins?
Superior margin: Frontal bone (medially: supraorbital notch)
Medial margin: Above by the frontal bone, below by the posterior lacrimal crest of the lacrimal bone and the anterior lacrimal crest of the maxillary bone
Inferior margin: Maxillary and zygomatic
Lateral margin: Zygomatic and frontal

What bones make up the orbital roof?
Orbital plate of the frontal bone
Lesser wing of the sphenoid

What bones make up the medial orbital wall?
Frontal process of the maxillary bone
Lacrimal bone
Orbital plate of the ethmoid
Lesser wing of the sphenoid

What bone makes up the largest portion of the medial wall?
Ethmoid
Describe the location of the lacrimal fossa
Formed by the frontal process of the maxilla and the lacrimal bone
Below is continuous with the bony nasolacrimal canal which extends into the inferior meatus (beneath inferior turbinate)

What is the lamina papyracea?
Paper thin medial wall of ethmoid bone
What bones make up the orbital floor?
Maxillary bone
Palatine bone
Orbital plate of zygomatic bone

Describe the path of the infraorbital groove
Traverses the floor of the orbit and descend anteriorly into a canal.
Exits as the infraorbital foramen, below the orbital margin of the maxillary bone.
It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve.

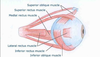
What is the only EOM that does not originate from the orbital apex?
Inferior oblique.
The inferior oblique arises from the orbital surface of the maxilla, lateral to the lacrimal groove. Unlike the other extraocular muscles (recti and superior oblique), the inferior oblique muscle does not originate from the common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn).

What is the slope of the orbital floor?
Downwards from posterior to anterior, 20 degrees
What fractures of the orbit are more common before puberty?
Trapdoor type fractures because the bones of the floor of the orbit are immature
What is the strongest orbital wall?
Lateral
What bones make up the lateral orbital wall?
- Zygomatic bone
- Greater wing of the sphenoid

What is Whitnall tubercle?
“Lateral orbital tubercle”
A small elevation of the orbital margin of the zygomatic bone approximately 11mm below frontozygomatic suture.
Because they all contain the letter L, I remember these structures as the “4 L’s”:
Lateral rectus check ligament
Lockwood suspensory ligament
Lateral palpebral ligament
Levator aponeurosis
Whitnall’s ligament does NOT attach to Whitnall’s tubercle.

Describe the location and structures associated with the optic foramen.
Leads from the middle cranial fossa to the apex of the orbit.
The optic foramen is the opening to the optic canal.
The canal is bound medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
Conducts the:
- Optic nerve
- Ophthalmic artery
- Sympathetic fibers from the carotid plexus
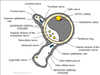
Describe the location and structures of the supraorbital foramen
Located at the medial third of the superior margin of the orbit.
Transmits blood vessels and supraorbital nerve (branch of the ophthalmic (V1) division cranial nerve V.
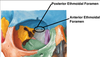
Describe the location and structures of the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramen
Located at the frontoethmoidal suture and transmits the anterior ethmoidal vessels and nerve.
Describe the location and structures of the zygomatic foramen
Lies in the lateral aspect of the zygomatic bone and contains the zygomaticofacial and zygomaticotemporal branches of the zygomatic nerve and artery.
(The zygomatic nerve (temporomalar nerve; orbital nerve) is a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2, itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve) that enters the orbit and helps to supply the skin over the zygomatic and temporal bones.
The zygomatic nerve arises in the pterygopalatine fossa. It enters the orbit by the inferior orbital fissure, and divides at the back of that cavity into two branches, the zygomaticotemporal nerve and zygomaticofacial nerve, which exit the orbit using identically named foramen.
The zygomatic nerve carries sensory fibers from the skin. It also carries post-synaptic parasympathetic fibers (originating in the pterygopalatine ganglion) to the lacrimal nerve via a communication. These fibers will eventually provide innervation to the lacrimal gland. These parasympathetic preganglionic fibers come from the facial nerve (CN VII).)

Describe the location and structures of the infraorbital canal
Continues anteriorly from the infraorbital groove and exits below the inferior orbital margin.
Transmits the infraorbital nerve which is a branch of V2 (maxillary division of CN V).