Gallbladder images Flashcards
(74 cards)
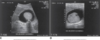
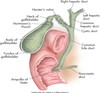
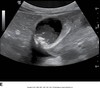
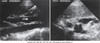
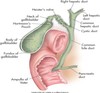
anatomy of gallbladder image

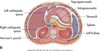
GB & biliary sysem
common bile duct image
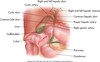
image hepatic lobules and sinusoids
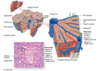
normal relational anatomy image
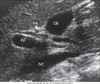
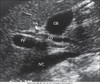
GB anatomy image
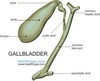

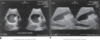
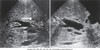
cross sectional- level of the 2nd lumbar vertebra

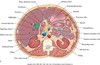
sectional anatomy level of 3rd lumbar vertebra
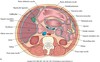

Sagittal section of the abdomen, 8 cm from the midline.

Sagittal section of the abdomen, 7 cm from the midline.


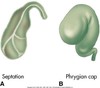
anatomic variants

Sonographic Evaluation of the Biliary System

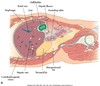
the main lobar fissure (MLF) is seen as an echogenic linear echo within the liver (L) connecting the right portal vein (PV) to the neck of the gallbladder (GB).

Main Lobar Fissure

-string connecting to PV; GB is the balloon; connects to GB neck

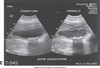
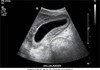
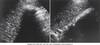
sag. GB


Trv. GB


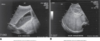
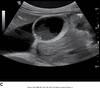
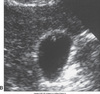
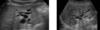
distended GB image

Distended GB
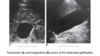
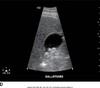
hydropic GB


contracted GB

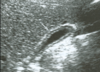
Hydrops of GB

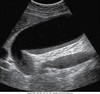
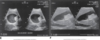
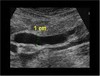
common bile duct image
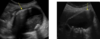
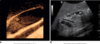
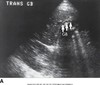
Transverse view of the common bile ducts. This view shows the portal triad with the portal vein posterior, the common duct anterior and lateral, and the hepatic artery anterior and medial.


common bile duct image

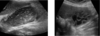
Sagittal image. The hepatic artery (HA) is shown anterior to the common ducts (CD). The portal vein (PV) is anterior to the inferior vena cava (IVC). GB, Gallbladder.

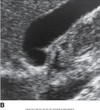
cystic duct image

Coronal decubitus view. The cystic duct seems to arise from the neck of the gallbladder (GB) (arrows). AO, aorta; IVC, inferior vena cava; PV, portal vein; L, liver.

sludge patterns
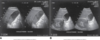
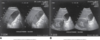
sludge patterns