Gastroenterology IV Flashcards
(16 cards)
What rare cancer is most closely associted with Celiac disease?
It is the result of proliferation of what type of cell?
T cell lymphoma
It is the result of proliferation of intraepithelial lymphocytes
What two cell types are located within the Crypts of Lieverkuhn?
- Paneth cells
- Progenitor cells
Where are Paneth cells located?
Describe their structure.
What is their function?
- location
- base of crypts of lieerkuhn
- structure
- columnar with eosinophilic granules
- lysozyme
- defensins
- TNF alpha
- also increases iCAM & selectin on WBC and endothelial cells (increase changes leukocytes to extravasate)
- columnar with eosinophilic granules
- function
- control
- bacteria
- control
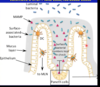
How can you identify progenitor cells?
Why are they so hard to identify?
Where are they located?
What is their function?
- identify
- mitotic figures
- they are hard to identify becaus theya re undifferentiate cells (replace any cytes in epithelium)
- bone marrow derived
- location
- crypts of lieberkuhn
- function
- replacement cells
What is the most distinctive component ofthe lamina propria of the small intestine?
What is the lamina propria composed of?
- Loose connective tissue
- MALT/GALT (mucosa/gut associated lymphoid tisue)
- diffuse lymphoid tissue (most distinctive)– in loose connective tissue
- leukocytes
- macrophages
- scattered lymphoid follicles (aggregated into nodule)
- duodenum and jejunum
- Peyer’s patch
- aggregated lymphoid follicles
- antimesenteric side
- ileum
- diffuse lymphoid tissue (most distinctive)– in loose connective tissue
How is blood supplied to the small intestine lamina propria?
- capillary loops
- from submucosa
- into villus
- collects soluble nutrients
- amino acids and sugars
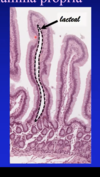
Describe the lympatic composition of the small intestine lamina propria
- lacteal (lymph looks milk b/c lots lipids in it)
- in villus
- blind-ended capillary
- collects chylomicra
- larger lymphatics
- in submucosa
What are the components of the submucosa of the small intestine?
- dense connective tissue
- vascular plexus
- Meissner’s plexus
- Brunner’s glands
- only in duodenum
- mucous glands
- branched tubular
- alkaline secretions
- neutralize gastsric acid
What are the components of the muscularis externa of the small intestine?
- muscularis externa
- inner circular layer
- outer longitudinal layer
- auerbach’s plexus
Which parts of the small intestine are covered wtih adventitia, whcih are covered with serosa?
- adventitia (retroperitoneal)
- most of duodenum
- serosa (intraperitoneal)
- jejunum
- ileum
- part of duodenum
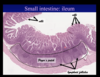
How can you identify the small intestine?
How cna differentiate between the different part of the small intestine?
- small intestine: villi
- duodenum
- submucosal glands
- fewest goblet cells
- jejunum (identify via exclusion)
- tallest villi
- ileum
- most goblet cells
- peyer’s patches
- short villi
- most goblet cells
- duodenum
What are the regions of the large intestine?
What are the functions of the large intestine?
- Regions
- cecum & appendix
- colon
- rectum
- anal canal
- functions
- reabsorption of
- electrolytes
- elimination of waste
- reabsorption of
- general struction same as rest of GI tract
What is unique about the mucosa of the large intestine?
Describe the components of the mucosal epithelium.
Submucosa?
- mucosa
- no villi!
- mucosal epithelium
- same cells as in small intestine
- no Paneth cells
- Goblet cell are abundant
- crypts of Lieberkuhn
- same cells as surface
- progenitor cells
- if you see Paneth cells, you are looking at an inflamed bowel
- Submucosa: same as small intestine
Describe the composition of the muscularis externa of the large intestine.
- Muscularis externa
- inner circular layer
- outer longitudinal lyer
- teniae coli – distincitive feature of the colon
- 3 thickened bands
- teniae coli – distincitive feature of the colon
What is interesting about the serosa of the large intestine?
omental appendices (small fatty projections)
What are the regional differences in the large intestine?
- colon
- largest part
- tenia coli
- vermiform appendix
- aggregted lymphatic nodules
- pr
- rectum
- transverse rectal folds
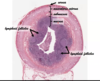
image is the appendix