Gram Positive Cocci Flashcards
(54 cards)
Most common Staphylococcal isolate in dogs
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
Disease and Cause

Ulcerative pododermatitis
Staphylococcus aureus
Disease and Cause

Jowl Abscess
Streptococcus porcinus
Disease and Cause
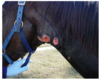
Strangles
Streptococcus equi subsp equi
Guttural Pouch Empyema
Accumulation of purulent material in guttural pouch
_____________________
Secondary to Strangles infection
Clinical sign of Strangle infection appear __________ after exposure
Clinical sign of Strangle infection appear 3-14 days after exposure
Diagnosis of Staphylococcal Infection
Direct Examination
Culture
PCR
Cause

Streptococcus suis
___________ is one of the most common nosocomial pathogens in humans.
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most common nosocomial pathogens in humans.
Guttural Pouch Chondroids
Accumulation of soft or hard concretions in one or both guttural pouches
______________________
Secondary to Strangles infection
Enterococcus sp inhabit the
GI tract
Enteroccous infections cause
persistent UTI
Serotype 2 of Streptococcus ________ is the most common isolate.
Serotype 2 of Streptococcus suis is the most common isolate.
First clinical sign to appear from a Strangles infection
Fever
__________________
39 - 39.5 C
Disease and Cause

Scarlet Fever
Streptococcus pyogenes
Causes Scarlet Fever in humans
Streptococcus pyogenes
Staphylococcal isloate that causes mastitis in cattle
Staphylococus aureus
Causes ulcerative pododermatitis in sheep and humans
Staphylococcus aureus

Staphylococcus sp
Structure of Streptococcus sp.
Pairs or chains
Problems associated with treating Staphylococcal infections
Reisistance!
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing is critical
___________________
Clindamycin, Macrolide, Methicillin
Classification of S. equi subsp equi
Beta-hemolytic, Group C
For an animal to be removed from quarantine after a Strangles infection, they must have
For an animal to be removed from quarantine after a Strangles infection, they must have 3 negative cultures at weekly intervals
Age of horses typically infected with Strangles
< 2 years old








