GUT Women's Health Anatomy & Radiology Part 2 (& Commentary) Flashcards
(60 cards)
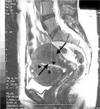
Know the structures on the slide

What is a a hysterosalpingogram and what is it used for?
- Injection of radiographic contrast goes into the cervical os to see the uterine cavity and if the fallopian tubes are open (normally open to the peritoneal cavity)
- For fertility studies
- Open uterine cavity means a chance for successful implantation of fertilized egg
Abnormalitites of the tubes and uterus can cause infertility such as?
- scarring in the uterus
- masses in the uterus
- scarring in the tubes 2/2 PID
Does VUR cause renal damage?
Not necessarily!
What is primary VUR?
- Genetic predisposition to short ureteral tunnel through the bladder
- Small chance of renal damage from VUR
What is secondary VUR?
- To the bladder and/or urethral dysfunction ie: neurogenic bladder or posterior urethral valves
- Have the most problems and have increased chance of renal damage
If there is no stasis of urine in the GUT does VUR predispose a patient to UTIs?
NO - VUR does not predispose if there is no stasis of urine
What is required if a Hydronephrosis is found on prenatal US?
Requires a f/u evaluation after birth to determine etiology
What percentage of children <5 y/o with UTI’s have VUR?
30-40%
What conditions increase the chance of renal scarring?
- Febrile UTIs
- VUR plus UTIs
T/F: Surgery to reimplant ureters and/or prophylactic ABX do not necessarily prevent UTIs and/or renal damage
True
Greater grade of reflux is associated with ___ chance of renal damage
increased
What is the bottom Line of VUR and UTIs?
They require individual evaluation and tx as these are complex entities with still evolving knowledge of their associations
Grading of VUR

What should a workup of VUR include? What are you evaluating?
- VCUG or Isotope Cystogram and a Radionuclide DMSA Renogram
- Evaluating renal parnchyma and presence of reflux
- In utero US evaluation is important to ID prenatally the presence of hydronephrosis and/or kidney size
What are the 2 causes/types of Vesicoureteral Reflux?
- Due to immaturity with a short ureteral tunnel in the bladder
- Due to a congenital anomaly at the UV junction
- no tunnel, adjacent bladder diverticulum, or displaced orifice
What happens in VUR if reflux is present with a UTI and the cause is a short ureteral tunnel?
- Pyelonephritis and renal damage can result
- An immature short tunnel usually resolves with age
What happens in VUR if reflux is present with a UTI and the cause is a congenital anomaly at the UV junction?
Same thing as a short ureteral tunnel - pyelonephritis and renal damage can result
*If reflux of any etiology is present with a UTI, pyelonephritis & renal damage can occur
Posterior Urethral Valves or a Neurogenic Dysfunctional Bladder does not necessarily occur if the ureteral tunnel is ___?
normal
*if the tunnel is abnormal, reflux occurs
When prenatal fetal hydronephosis occurs or the patient has documented pyelonephritis, VCUG or Radionuclide Cystogram, is indicated to determine what?
- If underlying anatomic or functional abnormalities are present
- If so, depending on findings, treat
In Hydronephrosis what will you see on VCUG or Cystomgram secondary to ureteral obstruction?
Dilated urinary collecting systems, calyces, infundibula, renal pelvis, ureters
High pressure in the urinary collecting system 2/2 to obstruction can cause?
rupture of the collecting system
*this is not a concern & spontaneously resolves
Bladder stone (bladder calculi) 2/2 to bladder urinary stasis and contributes to ___?
infection
What defects in the ureter and bladder indicate malignancy?
Filling defects