GYNO FINAL IMAGES Flashcards
(117 cards)
1
Q
*

A
Dermoid Tumor
-dermoid mesh
2
Q

A
Dermoid Cyst
-tip of the iceburg
3
Q
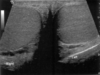
A
Testes
- low level echogenicity
- 7-10 mm diameter
- mediastinum teste and epididymus (not seen until after puberty)
4
Q
*

A
Bicornate Uterus
- best seen in trans
- bicornate and didelphys -not associated w/ infertility
- duplicated uterus w/ common cervix
5
Q
*

A
Bicornate Uterus
- best seen in trans
- bicornate and didelphys -not associated w/ infertility
- duplicated uterus w/ common cervix
6
Q

A
Uterus w/ Fibroids
- fibroid usually has rounded borders
- fibroids are estrogen dependant and grow during pregnancy
- may cause infertility
7
Q
*

A
submucosal fibroids
- look how each fibroid interfaces w/ endometrial lining
8
Q
*

A
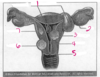
Uterine Polyp
- polyp outlined w/ SIS
- color doppler demonstrating vascular pedicle
9
Q
*

A
Uterine Polyp
(on a stalk)
10
Q

A
Uterine Synechia
- synechia shows up as linear strands of scar tissue extending from one side of uterus to other
11
Q

A
Follicles
- 1st image: follicular phase
- 2nd image: dominant follicle
12
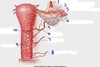
Q

A
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome“string of pearls”
- 12 or more follicles measuring 2-9 mm;
ovarian volume > 10 cm3
- often occurs w/ clinical triad:
- olgiomenorrhea, hirsutism, obesity
- immature follicles continue to produce estrogen and androgen which inhibits pit gland.
- Pit gland produces more LH than FSH –> follicle to remain in arrested state of development- no mature ova released w/ ovulation
- chronic elevation of estrogen

13
Q

A
peritoneal inclusion cysts
14
Q

A
endometriosis
- most common benign gynecologic disease
- in 10-25% of women w/ gyn disease
- in 40% of women w/ infertility
assess thickness and echogenicity pattern
increased thickness 2-3 mm –> 12-14 mm
- measure long plane
- outer to outer - double layer thickness
- normal pattern - trilaminar
- thin endometrium - < 8mm (in secretory phase)
- -decreased fertility
15
Q

A
measuring endometrium
16
Q

A
Ovarian Stimulation
- administer clomiphene (Clomid) or gonadotropin (Pergonal) day 3-5 in normal cycle
- enlarges multiple follicles instead of just one dominant follicle
- US monitors # and size of follicles day 8-14 (follicular phase)
- count all follicles > 1cm or 10mm
- optimum follcile size = 15-20 mm
- hCG may be given IM to trigger ovulation w/ retrieval 30-34 hours later
17
Q

A
Oocyte retrieval
- oocyte fertilization in dish and incubated for 3 to 5 days before embryo transfer
18
Q

A
US guided embryo transfer
19
Q

A
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
- this is a complication of assisted reproductive technology
- enlarged ovaries, multiple cysts, abd ascites, pleural effusions
- more common w/ PCOS
- mild ovarian enlargement 5- 10 cm

20
Q
A

A
interstitial/ cornual
21
Q
B

A
isthmus
22
Q
C

A
abdominal
23
Q
D

A
ampulary
24
Q
E

A
fimbrial
25
F

ovary
26
G

cornual/ interstitial
27
H

fornix
28
I

cervical
29
J

body of uterus
30
K

abdominal peritoneum
31
What is seen inside this double decidual sac sign?

yolk sac
32


33

interstitial pregnancy
* endometrial cavity line does not enlcose gestational sac
* absence of surrounding myometrium - pregnancy look like it is at the edge of the right side of uterus
* **most life threatening**

34

cervical ectopic pregnancy
35

**abdominal ectopic pregnancy**
* pregnancy develops w/in the peritoneal cavity

36
indications for 1st trimester exam
* Confirmation of IUP vs. EUP
* Define cause of bleeding
* Pelvic Pain
* Viability
* # of embryos
* Gestational age
* Detect anomalies
* R/O hydatidform mole
* Adjunct to CVS, amnio, embryo transfer, IUD removal
* \*\*First trimester exam performed only when deemed necessary\*\*
37
indications for 2nd & 3rd trimester exam
* Gestational Age
* Fetal Growth
* Vaginal Bleeding
* Abd/Pelvic pain
* Incompetent cervix
* Determine fetal presentation
* # fetuses
* Size discrepance to dates
* Pelvic mass
* Suspected hydatidform mole
* Cervical cerclage placement
* R/O ectopic
* Fetal viability
* Uterine abnormality
* Evaluate fetal well-being
* Amniotic fluid
* Placental abruption
* External cephalic version
* Premature rupture membranes and/or labor
* Abnormal chemical markers
* F/U fetal anomaly
* History prev congenital anomaly
* Eval for late to prenatal care
38
1.

uterine fundus
39
2

fallopian tube
40
3

fimbriae
41
4

myometrium
42
5

endometrium
43
6

uterine isthmus
44
7

lateral fornix
45
8

vagina
46
9

ectocervix
47
10

endocervix
48
11

ovarian ligament
49
12

ovary
50
benign smooth muscle cell tumor; few appear in the cervix

cervical leiomyoma (fibroid)
*

51
fluid filled uterus

hydrometra
52
blood filled.

hematometra

53
1
## Footnote
**leiomyoma locations**

pedunculated or intracavitary
54
2
leiomyoma locations

Ovary
55
3
leiomyoma locations

submucosal
56
4
leiomyoma locations

uterus
57
5
leiomyoma locations
cervix
58
6
leiomyoma locations

subserosal
59
7
leiomyoma locations

intramural
60
most common gynecologic tumor of childbearing age women, and is more common in black women?

**submucosal leiomyoma** (common location)
* fibroid is anterior & is pushing endometrium posterior
* smooth muscle cell tumor
* encapsulated with pseudocapsule
* fibrosis w/ degenerative changes
* out grow their blood supply and atrophy
* estrogen dependant
* pregnancy and tamoxifen = ↑ growth (size)
* menopause w/o HRT = ↓ growth (size)
* **Clinical findings**: irreg bleeding, menorrhagia, menometrorrhagia, enlarged uterus, infertility, pee alot
* **on US: (variable)** enlarged uterus w/ irregular wall, bright echoes w/ clcifications & shadowing, discrete mass

61
**very common** benign disease of the uterus; infiltration of endometrial tissue from stratum basalis into myometrium?

**adenomyosis**
* Ectopic endometrial tissue within myometrium
* More common posterior uterus
* Does not bleed with hormone cycle
* Product of multiple pregnancies
* Elevated estrogen levels
hypermenorrhea, menorrhagia, metrorrhea, dysmenorrhea
on US:
* Diffuse uterine enlargement
* Thickening posterior myometrium
* Small myometrial cysts - swiss cheese or honeycomb - non vascular
* Subendometrial cysts
* Myometrial heterogenicity with ill-defined endometrial borders
* May mimic fibroid
* MRI characterizes adenomyosis better

62
overgrowth of endometrial tissue covered by epithelium containing glands, stroma, blood vessels

uterine polyps
* peri & post menopausal women -more common & associated w/ bleeding
* menstruating women - asociated w/ infertility & menometrorrhagia
* differential: hyperplasia, submucosal leiomyoma, or endometrial cancer
* doppler shows a feeding artery in a pedicle
63

synechiae
* intrauterine adhesions (Asherman's Syndrome)
* found after trauma or surgery, uterine curettage
* cause of infertility or pregnancy loss
* better seen in gravid uterus, secretory phase
* adhesion bridging bands of tissue- thin membrane or thick broad based adhesion
* can be divided under hysteroscopy
64

IUCD in place
65
small endocrine structure that develops w/in a ruptured ovarian follicle and secretes progesterone and estrogen

corpus luteum cyst

66
requires 3 things: smooth walls, fluid filled, acoustic enhancement

simple cyst
is usually benign
67

corpus luteum cyst
68

ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)
* complication of ovulation induction
* **mild**
* pelvic discomfort, ovaries enlarged \< 5cm
* **severe**
* ****severe pelvic pain
* distended abd.
* ovaries enlarged \>10cm
* **ascites, pleural effusions**
* w/ treatment - resolves in 2-3 weeks
69
12 or more follicles measuring 2-9 mm and ovarian volume greater than 10 cm3

polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
* very common
* **"string of pearls"**
* stein leventhal syndrome
* infertility, oligomenorrhea, hirsutism & obesity
* bilateral enlarged polycystic ovaries
* common cause of infertility and miscarriage
* diagnosis usually made by hormone levels
70

endometriosis
* functional endometrial tissue present outside the uterus
* diffuse is more common
* localized = chocolate cyst
* bleeds cyclically

71

dermoid tumor
tip of the iceberg sign
72

dermoid cyst
dermoid mesh
73

hydrosalpinx
fluid in the fallopian tube

74
1
Blood supply to pelvis

internal iliac artery
75
2.
Blood supply to pelvis

tubal branch of uterine artery
76
3.
Blood supply to pelvis

ovarian branch of uterine artery
77
4.
Blood supply to pelvis

infundibulopelvic ligament
78
5
Blood supply to pelvis

ureter
79
6
Blood supply to pelvis

uterine artery
80
7
Blood supply to pelvis
vaginal artery
81
8
Blood supply to pelvis

internal pudendal artery
82
9
Blood supply to pelvis

azygos arteries
83
10
Blood supply to pelvis

cervical branch of the uterine artery
84
1
genital tract

uterine (fallopian) tube
85
2
genital tract

cornu
86
3
genital tract

fundus
87
4
genital tract

corpus
88
5
genital tract

isthmus
89
6
genital tract

cervix
90
7
genital tract

rugae of mucosal lining
91
8
genital tract

adventitia
92
9
genital tract

muscular wall
93
10
genital tract

mucosa
94
11
genital tract

vagina
95
12
genital tract

external os
96
13
genital tract

lateral vagina fornix
97
14
genital tract

internal os
98
15
genital tract

serosa
99
16
genital tract

myometrium
100
17
genital tract

uterine cavity
101
18
genital tract

endometrium
102
Uterine Position Variations

103
1
fallopian tube

mesosalpinx
104
2
fallopian tube

infundibulum
105
3
fallopian tube

fimbriae
106
4
fallopian tube

ovarian ligament
107
5
fallopian tube

interstitial portion
108
6
fallopian tube

isthmus
109
7
fallopian tube

ampulla
110
what endometrial phase is this "thin line"?

early proliferative
111
what endometrial phase is this "three line sign"?

classic proliferative
112
what endometrial phase is this thickened ?

secratory phase
113
what phase?
what position?

early secretory
retroflexed to the right
114
what phase?

secratory phase
115
what flexion?

anteflexed
116
what flexion?

anteflexed
117
what flexion?

retroflexed


