Heart Flashcards
(60 cards)
Coronary Sulcus
- groove on the external surface of the heart that marks the position of the interatrial septum
- conveys coronary vessels

Interventricular Sulcus
- groove on the external surface of the heart that marks the position of the interventricular septum
- conveys coronary vessels

Interatrial Septum
- internal partition between the right and left atria

Interventricular Septum
- internal partition between the right and left ventricles
- primarily made up of muscle with small area of membrane
- defects often located in membranous part of septum
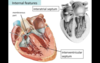
Crista Terminalis
- a ridge that separates the smooth part (der. sinus venosus) from the rough part (der. primitive atrium) of the right atrium
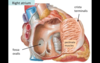
Pectinate Muscles
- comb-like muscular ridges found on the wall of part of the right atrium and within the left auricle
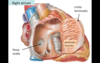
Fossa Ovalis
- an oval-shaped depression on the interatrial septum of the right atrium that marks the location of the foramen ovale that was present in the fetus

Valve of Foramen Ovale
- piece of tissue on the interatrial septum of the left atrium that is a remnant of the primitive interatrial septum in the embryo - septum primum
- valve typically completely fused with interatrial wall (although occasionally incomplete fusion causing a small opening in the interatrial septum)
Tricuspid Valve
- valve between the right atrium and right ventricle
- aka Right Atrioventricular Valve

Pulmonary (Semilunar) Valve
- valve between the conus arteriosus and the pulmonary trunk
- consists of three cup-like cusps that have a central thickening called a nodule that is imp for valve closure
- passively opened by blood flow during systole
- during diastole, blood falls back down outflow tract and collects in sinuses of semilunar valve, causing nodules to meet and form an inverted pyramid - prevents cusps from descending further and keeps valve closed

Trabeculae Carnea
- muscular bundles on the walls of the ventricles
Papillary Muscles
- muscles attached to the atrioventricular valve cusps via chordae tendinae
- function to hold valve closed during systole preventing the valve cusps from flapping back into atria
- DO NOT contract to open the valve
- i.e. opening is passive, closing is active*
Moderator Band
- band of muscle containing conductive tissue connecting the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle and the anterior wall of the right ventrical
- aka Septomarginal Trabecula
Conus Arteriosis
- the smooth outflow tract of the right ventricle leading to the pulmonary valve
- aka infundibulum
Bicuspid Valve
- aka Mitral Valve
- valve in the heart between the LA and LV
- aka Left Atrioventricular Valve

Aortic Valve
- aka Semilunar Valve
- the valve in the heart bw the LV and aorta
- has three cusps with a central nodule on each
**- opening for coronary arteries within two cusps
- passively opened by blood flow during systole
- passively closes during diastole (blood flowing back fills cusps and causes closure)

Auricles
- small ear-shaped appendages attached to the atria
- developmental remnants of primitive atria (no function)

Grooves on the external heart
- Coronary Sulcus - between the atria and ventricles
- Interventricular Sulcus - between the ventricles
Right Atrium
Receives blood from: SVC, IVC, Coronary Sinus
Features:
- Crista terminalis
- Pectinate muscles
- Fossa ovalis
- Openings for SVC, IVC, Coronary Sinus

Right Ventricle
Receives blood from: RA through tricuspid valve
Features:
- Trabeculae carneae
- Papillary muscles
- Chordae tendineae
- Septomarginal Trabecula (moderator band)
- Conus arteriosis (infundibulum)
- Pulmonary (semilunar) valve

Left Atrium
Receives blood from: four pulmonary veins
Features:
- Pectinate muscles
- Valve of the Foramen Ovale
- Openings of the four Pulmonary Veins

Left Ventricle
Receives blood from: RA through the mitral valve
Features:
- Trabeculae carneae
- Chordae tendineae
- Papillary muscles
- Aortic (semilunar) valve

Coronary Arteries
- two openings in the aorta within cusps of the aortic semilunar valve
- blood flows into the arteries when blood flows back into the sinuses of the cusps (i.e. during diastole)
Heart Shape
- cone
Base: posterior, superior, right
- LA, small part of RA, prosimal parts of great veins (SVC, IVC, pulmonary veins)
Apex: anteroinferior, left
- LV
- lies deep to the 5th intercostal space