Mediastinum Flashcards
(52 cards)
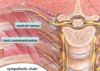
Mediastinum
- central region of the thoracic cavity
- contains the heart and great vessels

Transverse Thoracic Plane
- division of the mediastinum into superior/inferior portions by horizontal plane that passes through:
Anterior - Sternal Angle
Posterior - disc between T4-T5
Inferior Divisions of the Mediastinum
- anterior, middle, posterior divisions of the pericardium
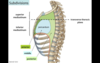
Borders of the Mediastinum
Superior - superior thoracic aperture
Inferior - diaphragm
Lateral - Pleural cavities and lungs
Anterior - sternum
Posterior - thoracic vertebrae

Pericardium
- pericardial sac - the membrane that surrounds the heart
Layers - outer fibrous layer and inner serous layer
- superior limit - transverse thoracic plane

Fibrous Pericardium
- tough outer layer of the pericardium that does not stretch
- fused to the diaphragm and continuous with the tunica adventitia of the great vessels

Serous Pericardium
Visceral Serous Layer - applied to the surface of the heart (forms outer layer of heart wall and can be called epicardium in that context)
Parietal Serous Layer - lines the internal surface of the fibrous pericardium
- both are continuous near the origins of the great vessels (i.e. fist in a balloon)

Pericardial Cavity
- potential space between the visceral and parietal serous pericardium

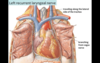
Great Vessels
- large arteries and veins connected to the heart
Includes - SVC, IVC, Ascending Aorta, Pulmonary Trunk, Pulmonary Veins
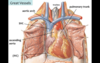
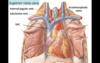
Superior Vena Cava
- large vein that receives venous drainage from the head, upper extremeties, and thorax
- drains into the RA
- convergence of the Left and Right Brachiocephalic Veins (Right Brachiocephalic Vein formed by convergence of Right Subclavian Vein and Right Internal Jugular Vein)
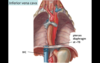
Inferior Vena Cava
- large vein that receives venous drainage from the lower half of the body (abdomen, pelvis, lower extremities)
- drains into the RA
- enters thoracic cavity by traveling through an opening in the diaphragm at T8
Aorta
- largest artery in the body
- arises from LV and immediately gives off Right and Left Coronary Arteries
In thorax, has 3 parts:
Ascending Aorta (ends at transverse thoracic plane)
Aortic Arch (begins and ends the transverse thoracic plane
Descending Aorta (aka thoracic aorta - begins at the transverse thoracic plane)
In abdomen: Abdominal Aorta - descends and bifurcates at L4 into common iliac arteries

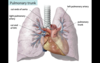
Pulmonary Trunk
- aka Main Pulmonary Artery
- outflow tract from RV
- bifurcates into right and left pulmonary arteries
Right Pulmonary Artery - travels posterior to ascending aorta and SVC towards Right Lung
Left Pulmonary Artery - travels anterior to the thoracic aorta
Pulmonary Veins
- four veins carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs to the LA

Thymus
- lymphoid organ involved in dev’t of immune system (T-cells)
- primarily active during childhood, undergoes involution during puberty and mostly replaced by fat
Location - posterior to the sternum, anterior to the great vessels and pericardium
Brachiocephalic Trunk
- the first branch of the aortic arch
- gives rise to the Right Sublcavian Artery and the Right Common Carotid Artery
- supplies upper right quadrant of the body
Left Common Carotid Artery
- second branch of the aortic arch
- supplies head and neck region
Left Subclavian Artery
- third branch of the aortic arch
- supplies the left upper quadrant of the body
Aortic Arch
- peak of the aorta bw ascending and descending aorta (above the transverse thoracic plane)
Three branches:
- Brachiocephalic Trunk
- Left Common Carotid Artery
- Left Subclavian Artery
* Remember you “ABCs” (Aorta, Brachicephalic, Carotid, Subclavian)*

Epicardium
- visceral serous layer of the pericardium that forms the outer layer of the heart
Ascending Aorta
- gives rise to the coronary arteries
- lies below the transverse thoracic plane

Descending Aorta
- aka Thoracic Aorta
- begins at the transverse thoracic plane
- descends anterolateral to the left of the vertebral column
- passes posterior to the diaphragm and becomes abdominal aorta from T12-L4 until it bifurcates
Ligamentum Arteriosum
- remnant of the ductus arteriosis (channel bw the pulmonary trunk and aortic arch that allowed blood to bipass lungs in fetus)
- fibrous after closure of ductus arteriosis at birth
- location between aortic arch and pulmonary vessels called “Autopulmonary window” by radiologists

Trachea
- posterior to the great vessels in the midline
- bifurcates into right and left main bronchi at T4 vertebral level