Hematopoiesis Flashcards
(21 cards)
Blood cell formation in the BM in what bones?
All cells are derived from a single what?
Skull, ribs, sternum, vertebrae, pelvis, proximal femurs
Pluripotent hemopoietic stem cell (HSC) –> Monophyletic Theory

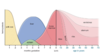
Hematopoietic Phases
Starts in fetus during 1st trimester with Hematopoietic islands of hematopoiesis in what structure?
Islands develop from what?
Process continues after 2nd trimester where?
During the 7th month/3rd trimester, what becomes primary site of hematopoiesis?
Umbilical vesicle/yolk sac
Hemangioblasts (progenitors of hematopoietic and endothelial cells)
Liver and spleen
Bone marrow
Bone Marrow
BM consists of what?
What makes up the sinusoid?
What do sinusoids separate?
Adventitial cells function and what do they produce?
Blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, and sinusoids
Endothelial lining, discontinuous basement membrane, & incomplete coving of adventitial cells
Hematopoietic compartment and peripheral circulation
Provide support for developing blood cells and produce reticular fibers & secrete cytokines

BM-Sinusoidal System
Describe the steps for newly formed blood cells to enter circulation
- Maturing blood cell/megakaryocyte process pushes against endothelial cell
- Fuse and pierce luminal plasma membrane (endothelial cell) –> forming opening
- Each blood cell/process squeezes through aperture and enters sinusoidal lumen
- Endothelial cell “repairs itself” and aperture disappears

Red Bone Marrow
Location?
Hematopoietic cords predominantly develop what?
What else is present in BM?
RBCs and Megakaryocytes develop where?
Granulocytes develop where?
Medullary cavity of young long bones and spaces of spongy bone
Blood cells & megakaryocytes
Macrophages, mast cells, & adipose tissue
Near sinusoidal wall
Father from sinusoid wall
Yellow Bone Marrow
Predominantly what type of cell?
Location?
Ratio of cell type?
Yellow BM retains hematopoietic potential and can convert back to red marrow, how does it repopulate with cells?
Adipose cells
Medullary cavity of adult bones no longer hematopoietically active (ribs, vertebrae, pelvis, shoulder girdle)
50:50, adipose:hematopoietic tissue
Repopulation by circulating stem cells
Cellularity of Bone Marrow
How to calculate normal cellularity?
Hypocellular marrow
Hypercellular marrow
Subtract age from 100 and adding +/- 10%
Small number of blood forming cells (aplastic anemai, chemotherapy)
BM affected by hematopoietic cell tumors (acute myelogenous leukemia)

Hematopoietic Growth Factors
Function?
Produced where?
Three Major Groups
Control proliferative and maturational phases of hematopoiesis
BM by endothelial cells, stromal cells, fibroblasts, developing lymphocytes, and macrophages
- Colony-Stimulating Factors (CSF)
- Erythropoietin (EPO) & Thrombopoietin (TPO)
- Interleukins (Cytokines)
Interleukins
IL-3
IL-2
IL-1 & IL-4
IL-2 & IL-6
Influences replication and growth potential of hematopoietic progenitors
T-Cell growth factor
Acts on pluripotent SCs to develop lymphoid SCs
B-Cell growth factor
EPO
TPO
Stimulates formation of RBCs - Produced primarily in kidneys
Stimulates increase in megakaryocytes and platelets - Produced in liver
CSFs (Colony Stimulating Factor)
GM-CSF (Granulocyte-Macrophage CSF)
G-CSF (Granulocyte CSF)
M-CSF (Macrophage CSF)
Produced by endothelial cells, T Cells, fibroblasts, and monocytes –> Stimulates formation of WBCs and reticulocytes
Produced by endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages –> Stimulates increase in neutrophils
Stimulates increase in monocytes and macrophages
HSCs
HSCs differentiate into multipotential progenitor cells
CMP differentiate into what?
Common Myeloid Progenitor (CMP) cells & Common Lymphoid Progenitor (CLP) Cells
Lineage-restricted progenitors
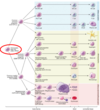
CMP Lineage Restricted Progenitors
CMP gives rise to?
- MEP (Megakaryocyte/Erythrocyte Progenitor)
- Megakaryocyte-committed progenitor cells (MEP, CFU-Meg)
- Erythrocyte-committed progenitor cells (ErP, CFU-E)
- GMP (Granulocyte/Monocyte Progenitor)
- Neutrophil progenitors (NoP, CFU-G)
- Eosinophil progenitors (EoP, CFU-Eo)
- Basophil progenitors (BP, CFU-Ba)
- Monocyte progenitors (MoP, CFU-M)
Erythropoiesis
Regulated by what?
Acts on surface receptors of what?
Common Myeloid Progenitor –> ___ –> ___
What is required for terminal differentiation to erythroid lineage?
Erythropoietin (EPO) - kidneys due to decreased SpO2
Erythrocyte Progenitor (ErP)
CMP –> Megakaryocyte Erythrocyte Progenitor (EPO, IL-3, IL-4) –> ErP
GATA-1

Erthryopoiesis
ErP –> ___ (large, cytoplasm is basophilic) –> ___ (polyribosomes synthesizing Hb) –> ___ (distinct pink and purple regions) –> ___ (increased acidophilic cytoplasm, dense nucleus, no longer capable of division) –> ___ (few polyribosomes synthesizing Hb retained, if RBCs increase, this increases) –> RBC
Proerythroblast
Basophilic erythroblast
Polychromatophilic erythroblast
Orthochromatophilic erythroblast
Polychoromatophilic erythrocyte (reticulocyte)
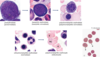
Thrombopoiesis
What influences differentiation of MEP?
Becomes further committed as what?
Forms what?
What process is unique to this?
GM-CSF and IL-3
MKP (Megakaryocyte-committed progenitor cell)
Megakaryocyte
Succesive endomitoses (increase in size/DNA but no cytokinesis)

Granulopoiesis
Originate from what?
Differentiates into what?
Stimulates production of what cell types?
EoPs require what?
BaPs require what?
Multipotent, CMP
Granulocyte/Monocyte Progenitors (GMPs) - GM-CSF and IL-3
Neutrophil, Eosinophil, Basophil, and Monocytes
GM-CSF, IL-3, IL-5
GM-CSF, IL-3

Granulopoiesis Stages
___ (large, intensely basophilic) —> ___ (large spherical nucleus with granules) —> ___ (initially spherical nucleus –> develop indentation) —> ___ (nuclear indentation deepens) —> ___ (nucleus is elongated and nearly uniform)
Mature neutrophil = ___
Myeloblast —> Promyelocyte —> Myelocyte —> Metamyelocyte —> Band Cell
Polymorphonuclear or segmented neutrophil

Neutrophil Shifts
Immature neutrophils enter what?
From this location where do they go?
Sudden and extremely severe infections: what happens?
Left shift?
Right shift?
Reserve pool in BM (5 days)
50% of band forms will circulate; 50% adhere to endothelial walls (marginated pool)
Reserve granulocytes drained faster than production can replace them
Band cells, metamyelocytes, and myelocytes enter circulation
Increase in mature blood cells
Monocyte Development
Develops from GMP (Granulocyte Monocyte Progenitor) into what?
Differentiation depends on what?
Further differentiation into what?
What happens in tissues?
Monocyte Progenitor Cell (MoP)
PU.1, Egr-1, IL-3, GM-CSF
Promonocyte –> Divide as they develop into monocytes
Differentiate into macrophages (GM-CSF, M-CSF)
Lymphopoiesis
Lymphocytes and NK cells develop from what?
1st identifiable progenitor of lymphoid cells is what?
T-lymphocyte development in thymus depends on what?
B-lymphocyte development in BM depends on what?
Common Lymphoid Progenitor Cell (CLP)
Lymphoblast –> Divide 2-3 times into lymphocytes
Ikaros, GATA-3
Ikaros, Pax5


