Lymphoid Tissue Flashcards
(35 cards)
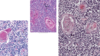
Neutrophils
What is their function?
Physical description?
What does polymorphonuclear mean?
Recognize & bind to Bacteria, foreign organisms, and infectious agents; Acute inflammation & tissue injury
Multi-lobed nucleus with lack of cytoplasmic staining
Varying shapes of nucleus
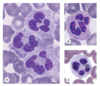
Eosinophils
Description of nucleus and cytoplasm?
What would cause increased counts?
- Bi-Lobed nuclei, Cytoplasm stains pink/red
- Increased counts with allergies and/or parasitic infection

Basophils
Nucleus?
- Lobed nucleus usually obscured by granules
Lymphocytes: Functional Cells of Immune System
Description of nucleus & cytoplasm
- Spherical nucleus w/ thin, pale blue rim of cytoplasm

Monocytes: Largest WBC
Description of nucleus?
- Heart/Kidney shaped nucleus

Primary and Secondary Structures
Functions
- Primary: Thymus & Red Bone Marrow
- Produces lymphocytes to recognize Ags
- Secondary: Diffuse lymphoid tissue
- Lymphocytes activated in response to antigens
Diffuse Lymphoid Tissue
Capsule status
Location
Function
Non encapsulated
Lamina Propria (GI, Genitourinary, Respiratory) - Subepithelial tissue
Intercept Ags and initiate immune response

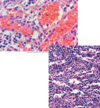
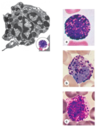
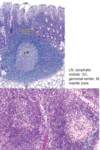
Nodular Lymphoid Tissue
Lymphatic nodules
Primary nodule
Discrete concentration of lymphocytes (non-encapsulated)
Consist of small lymphocytes without germinal center

Secondary Nodule/Follicle
Germinal Center
Mantle Zone (Corona)
Activated primary nodules exposed to Ag
Central region of nodule (lightly stained)
Outer ring of small lymphocytes encircling germinal center
Aggregated Lymphoid Tissue
Locations?
Tonsils
Peyer’s Patches
Veriform Appendix
Mucosa-Associated Lymphatic Tissue (MALT)
Tonsils
Location
Mucosa of posterior oral cavity, oropharynx, nasopharynx
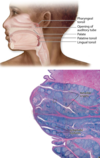
Palatine Tonsil
Lined with what type of epithelium?
What are the deep invaginations called?
What acts as partial capsule?
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Tonsillar crypts
Dense CT
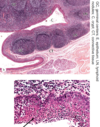
Pharyngeal Tonsil
Location?
Covered with what type of epithelium?
Capsule and crypt status?
Posterior wall of nasopharynx
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
Thin underlying capsule, no crypts
Lingual Tonsil
Location?
Covered with what type of epithelium?
Possess what structures not present in pharyngeal tonsils?
Capsule status?
Base of tongue
Stratified squamous epithelium
Germinal centers and varying number of crypts
No capsule
Peyer’s Patches
Location
Associated with what?
Covered with what epithelium?
SI (Ileum)
Intestinal villi
Simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells
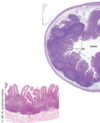
Veriform Appendix
Lamina propria infiltrated with what?
Type of epithelium?
Characterized by what?
Lymphocytes
Simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells
Crypts but no villi

Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)
Structure?
Lumen open to what?
Single/clusters of lymphoid nodules
External environment

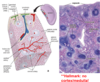
Lymph Nodes
Structure?
Comprised of what tissue?
Locations
Encapsulated structures positioned along lymphatic vessels
Reticular tissue
Axilla, Neck Vasculature, Thorax, Inguinal
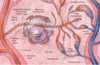
Lymph Nodes
Parenchyma
Stroma
Superficial Cortex
Deep (Para) Cortex
Medulla
Lymph Flow
Hilum
Cortex + Medulla
Supportive CT
Receives lymp from afferent lymphatic vessels
Region between cortex and medulla
Sinuses converge at efferent lymphatic vessel
Exit for efferent lymphatic and exit/entry for neurovasculature
Afferent –> Cortex –> Paracortex –> Medulla –> Efferent
Exit for efferent lymphatic and exit/entry for neurovasculature

Lymph Node Cortex
Superficial Cortex: what is located here?
Deep Cortex
- Superficial
- Location of lymphatic nodules (1 & 2)
- Immune cells suspended on reticular fibers
- Deep
- Free of nodules and high in T-cell counts

Reticular Meshwork
Cells of reticular meshwork?
Reticular cells
Dendritic cells (APCs) and Follicular DCs
Macrophages
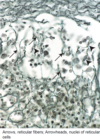
What are High Endothelial Venules?
What do they facilitate?
What leave circulation through these?
Postcapillary venules lined by cuboidal or columnar endothelial cells
Movement of lymphocytes from circulation and into lymph node via diapedesis
B cells and T cells

Lymph Node Medulla
Inner part of the LN, consisting of cords of lymphatic tissue called _ that are separated by _
What serves as the framework of the parenchyma?
Converge where?
Medullary cords; Medullary sinuses
Network of reticular cells and fibers traversing the medullary cords and sinuses
Near the hilum and drain into efferent lymphatic vessels

Thymus
What invade the tissue to proliferate?
What is involution?
Lymphoblasts
Decreased activity of thymus and becomes filled with adipose tissue over time