High Yield Flashcards
(170 cards)
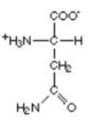
polar (hydrophilic) amino acids
threonine, serine, cysteine, asparagine, tyrosine, glutamine
PolariThree serene sisters aspire to tyranny and gluttony
Negatively charged (acidic) side chains
aspartic acid (aspartate) and glutamic acid (glutamate)
Positively charged (basic) Side chains
arginine, lysine, histidine
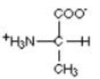
Nonpolar Hydrophobic amino acids
G, L, A, V, I, M, P, W
GWAIL-VMP
ectoderm
Nervous system, epidermis, lens of eye, inner ear, adrenal medulla, pineal and pituitary glands epithelia; neural crest
endoderm
Lining of digestive tract, lungs, liver and pancreas, urethra, urinary bladder, reproductive system; thymus, thyroid and parathyroid glands
Mesoderm
Muscles, skeleton, circulatory system, gonads, kidney; notochord, adrenal cortex
Aldosterone
- effect on Na+, K+ H+, and H2O
- secreted by
- is regulated by
- triggered by … in the
- what kind of hormone is it?
Aldosterone:
- stimulates Na+ reabsorption, K+ and H+ secretion,
- increases water reabsorption, blood volume, and blood pressure
- secreted by adrenal cortex
- regulated by the renin- angiotensin-aldosterone system
Steroid hormone
Triggered by low blood volume in the afferent arteriole
Increaes Na+-K+ pump activity
Increases blood volume
ADH (Vasopressin)
- function
- affect on H2O
- secreted from where and in response to what?
- what kind of hormone is it?
Increases collecting duct’s permeability to water to increase water reabsorption
• Is secreted from posterior pituitary with high [solute] in the blood
Peptide hormone
triggered by high plasma osmolarity
Opens aquaporins; reduces plasma osmolarity
James Lange
stimulus -> nervous system arousal -> conscious emotion
cannon bard
stimulus -> nervous system arousal + conscious emotion -> action
Scachter-singer
stimulus -> nervous system arousal + cognitive appraisal -> conscious emotion
TRP operon
is repressible (normally on, but can be turned off)
impact on Km- mixed
increases = prefer enzyme decreases = prefer complex
sucrose is also known as
glucose-α-1,2-fructose
lactose is also known as
galactose-β-1,4-glucose
maltose is also known as
glucose-α-1,4 glucose
Euchromatin
less dense, transcriptionally active dNA
Central dogma
DNA -> RNA -> proteins
Explain the difference between primary and secondary active transport
primary uses ATP while secondary uses existing ion gradients
rate limiting step of glycolysis
PFK1
location of TCA
mitochondrial matrix
ETC takes place in the…
inner mitochondrial membrane
pentose phosphate pathway occurs in the…. generates.. rate limiting step… activated by… inhibited by…
Pentose phosphate pathway: - occurs in the cytoplasm - generates NADPH and sugars - Rate limiting enzyme is G6PD - activated by NADP+ and insulin - Inhibited by NADPH