Histology Flashcards
(140 cards)
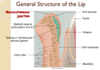
Name the three layers of the skin
- Epidermis
Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
Keratinocytes = true epithelial cells
- Dermis
Dense irregular connective tissue
- Hypodermis
Addipose tissue
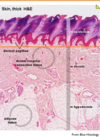
Explain how you would distinguish between thick and thin skin?
Thick skin
- lacks hair follicles
- nasal planum, footpads
- has both stratum lucidum and stratum corneum layers
Thin skin
- most frequent and is usually haired
- no strtum lucidum

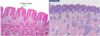
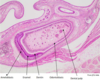
Identify all five layers of the epidermis ?
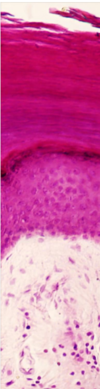
- Stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum corneum

Identify and describe the Stratum basale ?

Stratum basale
- single row of cells sitting on a basement membrane
- stem cells undergo mitosis
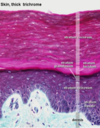
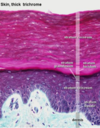
Identify and describe the Stratum Spinosum ?
Spinosum
- cells have spines projecting (cytoplasmic extension) and attach to each other via desomeres

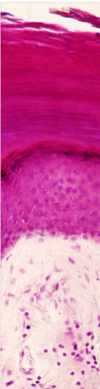
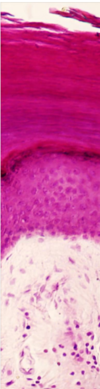
Describe and identify the Stratum Granulosum ?

Stratum Granulosum
- keratin accumulates in cells
- contains keratohyaline granules - start to bind keratin together and Lamella granules - water proofing
Describe and identify the Stratum Lucidum ?
Stratum Lucidum
- contains a protein which has a different staining affinity
- above granulosa layer, only in thick skin
- flattened dead cells of poor staining quality

Describe and identify the stratum corneum ?
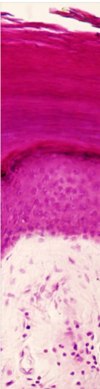
Stratum Corneum
- consisting of dead accumulated, anucleated squamous cells containg keratin
- layers depend upon the site of tissue
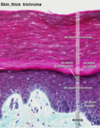
Explain what the epidermis is composed of and where it is located ?
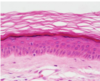
Epidermis
- the most superficial layer of squamous epithelium
- accompanied by other cell types for pigmentation, sensory perception and immune function
- derived from ectoderm layer of the trilaminar germ disc.
Keratinocytes = true epithelial cells
Describe Langerhans cells their location, function and structure ?
Langerhans cells
- found at the level of the stratum spinosum
- involved in immune function
- function as antigen presenting cells and may stimulate T cell responses in various allergic or inflammatory responses
- well characterised in humans and rodents
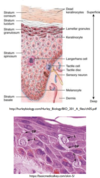
Describe what melanocytes do, their location and function ?
Melanocytes
- reside in the stratum basale layer of the epidermis
- originate in the neural crest of the ectoderm
- pigments may travel from basal layers to upper layers through specific processes - eventually phagocytosed by keratinocytes
They function to absorb and scatter UV radiation thus decreasing mutagenic effects
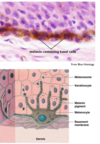
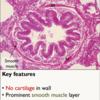
Describe the dermis, its location, composition and two layers ?
Dermis
- Located beneath the epidermis
- able to withstand certain mechanical stressers as it is both flexible and elastic
- thick layer of connective tissue
- dense irregular connective tissue
- contains blood vessels, lymphatics and inflammatory cells (histamine and heparin).
- develops from mesoderm of the trilaminar disc
Papillary layer = fine collagen fibres richly supplied with cappillaries
Reticular layer = Highly thick collagen bundles

Describe the location and composition of the Hypodermis ?
Hypodermis

The majority of the tissue is composed of adipose
but there are also, sweat glands, hair follicles, large vessels, nerves and lymphatics, skeletal muscle, mammary glands etc
Sebacious glands what do they produce, where are they located and what are they derived from ?

Sebacious glands (holocrine)
- derived from the epidermis
- solidly packed cells with a foamy appearance
- produce sebum an oily product that waterproofs or softens the hair
- glands empty into upper regions of hair follicles
- all the contents of the cell are lost to the cells surface

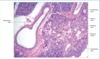
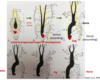
Describe hair follicles origin, and accompanying cells.

Hair follicles
Specialised down growth of the epidermis that extends deeply into the dermis and hypodermis
- hair growth originates at the bulb
- melanocytes provide pigment to matrix cells which are eventually formed into hard keratine
- arrector pilli muscles = smooth muscle attached to root sheath allow hair to become erect when cold

Identify the dermal root sheath, external root sheath, internal root sheath, hair and cuticle in a hair follicle ?

Describe the three stages of hair growth Anagen, Catagen and Telogen ?
Anagen
- Growth phase
- Dermal papilla (uppermost layer of the dermis) reattaches to a new hair follicle
- older hair pushed out by the growth of a new hair follicle
Catagen
- The dermal papilla detaches and rests, while the hair shaft is freed from the blood suplly and pushed upward
Telogen
- Dermal papilla reattaches to new hair follicle (Dose not grow)

Describe Apocrine glands and what they produce ?
Apocrine glands
- located throughout the skin of most domesticated animals
- empties into upper part of hair follicle
- simple cuboidal epithelium, coiled glands
- not true sweat glands produce = viscous fluid, sexual attraction, communication, territorial marking
- excretes a small portion of the cell contents and secretion
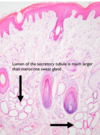
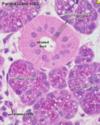
Describe Merocrine sweat glands and what they produce ?

Merocrine sweat glands ?
- simple cuboidal or columnar epithelium
- produce aqueous sweat for thermoregulation
- open directly onto the surface of the skin
- only secretion is lost to the cell surface
Found
- footpad of dog and cat (picture attached)
- frog of horse
- planum rostrale and carpal glands of pig
- nasolabial region in cattle

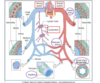
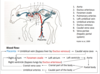
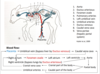
Describe the blood supply to the skin ?

Describe the formation of hooves, horns and claws ?
Hooves, horns and claws

Same structures as thick skin
They differ through the shape of the papillae / lamellae that extend from the dermis
Flat papillae = form flattish thick skin
Shaped papillae = form keratinised columns hooves, horns and claws
The hoof/ horn is held to underlying tissues through laminae
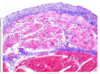
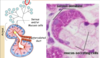
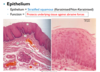
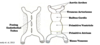
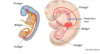
Identify the three layers of skin in a pigs ear, what features make this a thin skin classification ?
Pig ear thin skin
Thin skin as it lacks a stratum lucidum layer and contains many hair follicles
- blue = hypodermis
- pink = dermis
- purple = epidermis
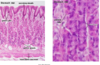
Identify the four layers of the epidermis in the thin skin of a pigs ear ?

Epidermis
yellow = stratum basale
blue = stratum spinosum
green = stratum lucidum
orange = stratum corneum
Identify the five skin layers in a dogs paw pad, what characteristics make this thick skin ?

Dog paw pad
This is thick skin as it has an incredable thick keratinous layer composed of stratum lucidum and stratum corneum (usually lacks hair follicles)
yellow = stratum basale
blue = stratum spinosum
green = stratum granulosum
purple = stratum lucidum
orange = starum corneum