Histology: Glands and secretion Flashcards
(175 cards)
Organs in the human body that would be made up of epithelial cells that function mainly to produce and secrete various macromolecules.
Glands
___can be used in the body or they can be discharged into the surroundings
Macromolecules
Macromolecules that are useful
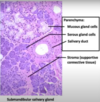
secretions from pancreatic gland
salivary gland
Macromolecules that can be discharged
secretions from the sweat glands
Functions of glands
Synthesize, store and release proteins, lipids, complexes of carbohydrates and proteins
secretes substances mainly made up of proteins
Pancreas
secretes lipids
Adrenal and Sebaceous glands
secretes complexes of carbohydrates and proteins
Salivary gland
secretes milk which is actually composed of all of the above substances (proteins, lipids, complexes of carbohydrates and proteins)
Mammary gland
Some glands have ____ activity and secrete mostly ___ and ____
little synthetic
water and electrolytes
Elaboration or release or discharge of fluids by epithelial cells containing various substances usually mucin, enzymes or hormones needed by the body
Secretion
Secretion does not require expenditure of energy (ATP) thus work is performed, T/F
False- requires
Elaboration or release of waste products not
needed by the body
Excretion
T/f, Excretion doesn’t require energy therefore no work is
Performed
true
Epithelial linings of internal body surfaces
lubricated by mucin
Mucous membranes
___is a product of combination of water and glycoprotein (mucin
Mucus
a.k.a. scattered secretory cells
UNICELLULAR GLANDS
T/F, Secretory cells are not distributed among non-secretory cells
False- distributed
Class of glands common in columnar, cuboidal and pseudostratified epithelium
UNICELLULAR GLANDS
Example of Unicellular glands
Goblet cells
important component in the lining of the intestines (columnar epithelium) and respiratory tract (pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)
Goblet cells
Secretes lubricating mucus that aids in the function of the intestines and respiratory tract
Goblet cells
Developed from the covering epithelia in the fetus by self-proliferation and growth in the underlying connective tissue followed by further differentiation
MULTICELLULAR GLANDS
Formed by invagination of epithelial layers in deeper tissue to form a diverticulum
MULTICELLULAR GLANDS