How we see 2 - transduction Flashcards
(13 cards)
What is phototransduction?
The conversion of light energy to an electrochemical response by the photoreceptors of the retina (rods and cones)
What is the role of photoreceptors (rods and cones) once activated?
The phototransduced rods and cones need to activate optic nerve cells (generate an action potential)
Identify the labels on this lovely diagram of a rod and cone.

JP domestically abuses women

Describe the structure of the lamellae found in rods and cones
Each lamella is made of cell membrane with some extra stuff integrated into it:
Cones:
- Cone opsins
- S (short) - Blue 437 nm
- M (med) - Green 533 nm
- L (long) - Red 564 nm
Rods:
-
Rhodopsin (a visual pigment)
- Low Green 498 nm

Describe the structure of Rhodopsin
2 bits:
- Opsin - Helical protein that is integrated into the membrane
-
11-cis Retinal - Vitamin A compound
- Nestled inside the Opsin
- This is the part that ‘reacts’ to light hitting the rod
How does Rhodopsin react when light hits? Shown below is the resting version of 11-cis retinal
What is the effect of this?

When light falls on 11-cis retinal, it isomerises to form ‘all-trans-retinal’
All-trans-retinal can not fit inside Rhodopsin so rhodopsin splits
The effect of this is Bleaching of the visual purple

What links the bleaching of purple by rhodopsin to phototransduction?
The Phototransduction cascade
“highly amplified cascade of light-triggered changes in protein conformation, and changes in interactions of proteins with one another and with guanine nucleotides”
Photoreceptor cells are kinda different from other cells in terms of their state (polarity) when they are at rest
How is this?
Unlike other cells in the body, the photoreceptor cells are, at rest (in the dark), kept in a depolarised state by open Na+/Ca+ channels
Complete the diagram of the phototransduction cascade
(its a bit aids but cba typing it all)

General idea:
- Photon of light = bunch of reactions
- Reactions = Na+ channel closes = hyperpolarisation
- Transmission through Ca2+ flux to bipolar cell synapse
Why is Vitamin A so important in the visual pigments?
Used in visual pigment regeneration
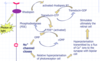
Complete the diagram showing how pigment regeneration works


What are the effects of vitamin A deficiency?
Night blindness (ie struggle to see in low levels of light)
Vitamin A is also essential for healthy epithelium. So conjunctiva and corneal epithelium are also abnormal.
Causes by malnutrition as well as coeliacs, sprue etc
What are the signs of vitamin A deficiency?
Bitot’s spot
Corneal ulceration
Corneal melting - (Which leads to future opacification of the cornea)



