Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles lecture 6 Flashcards
(75 cards)
Sperm production takes place in the ____________. Each testis contains ~500 coiled tubules called ________________ – that produce hundreds (thousands?) of sperm each second in healthy males.
1) testes
2) SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES
The inner lining of each tubule is lined with germinal tissue ( germinal means it’s gonna create something) – germinal tissue includes two kinds of cells knowns as
1)
2)
1) Germ cells
2) SUSTENTACULAR (Sertoli or Nurse) CELLS
•GERM CELLS goes through _________, these cells produce haploid sperm cells. All four resultant cells are viable sperm cells.
1) meiosis
•SUSTENTACULAR (Sertoli or Nurse) CELLS – nourish and __________________. They also secrete lubricating fluid to aid outward movement of sperm as they exit testis via ______________ and eventually epididymis. Also produces AMH (__________________), which regulates other hormones (e.g. testosterone, estradiol)
1) protect germ cells (so they can undergo meiosis)
2) efferent ductules
3) anti-Mullerian hormone
After it’s secreted by the sustentacular cells, the _______________ causes the “regression تراجع” of the paramesonephric duct.
anti-Mullerian hormone
Between seminiferous tubules there are clusters of endocrine cells called ____________ (aka ‘LEYDIG’) CELLS.
INTERSTITIAL
These cells secrete male sex hormones – ANDROGENS, the most important of which is __________________.
TESTOSTERONE
Sperm cells are amongst the smallest in the body (~1/20 mm).
Simple construction: __________________.
Tail is a flagellum – whipping motion provides ____________.
Base of tail contains a coiled _______________ to provide power for movement.
1) head and tail
2) motility
3) mitochondrion
Sperm Head contains nucleus and an organelle called an _____________ which contains digestive enzymes that helps sperm to penetrate egg (if present).
1)ACROSOME (a combination of vesicles diffused together)
Seminiferous tubules lead into straight tubules, then into larger set of tubules called _______________.
RETE TESTIS
Rete testis ultimately drains into larger tubules called ______________, which in turn drain into ____________.
1) efferent ductules
2) EPIDIDYMIS
Epididymis includes _________, ________ , and TAIL.
Tail of epididymis dilates (expands) into _______________.
1) HEAD
2) BODY
3) DUCTUS DEFERENS
Epididymis is a site of __________ storage
sperm (it’s not motile)
Epididimis secretes an enzyme that ___________________ of sperm that it can’t move.
Prevents the capacitence
DUCTUS DEFERENS passes up spermatic cord, and into body through _______________.
Inside body, right and left ductus deferens pass __________ over ureters, then loops _________ to them behind the urinary bladder.
1) inguinal canal
2) cranially
3) dorsal
As each duct passes behind (dorsal to) bladder, it has appended to it a gland called the ________________.
SEMINAL VESICLE
Just prior to attachment of the seminal vesicle, the ductus enlarges into an ________, which is a position of sperm storage prior to ejaculation.
AMPULLA
Notice how the spermatic cord loops ventral to (“in front of”) the attachment of the ureter of the bladder.
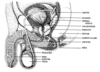
SEMINAL VESICLE has the enzyme which causes ______________ of the sperm
the capacitence
SEMINAL VESICLE
- Plastered up against the dorsal side of ____________.
- Exocrine glands - provide secretions that make up most of _____________.
- Fluid lubricates path of exiting sperm.
- Fluid is energy-rich (sugar rich) , providing food for sperm which is called _________.
1) urinary bladder
2) seminal fluid
3) Fructose
SEMINAL VESICLE Secretions is slightly __________. it helps to neutralize slightly acidic environment of vagina.
alkaline
_______________ promotes uterine contractions to help facilitate sperm movement up uterus into fallopian tubes.
___________ forms a temporary clot in vagina.
Once beyond the seminal vesicle, ductus is referred to as the ejaculatory duct. These are paired structures which empty into the prostatic urethra.
1) PROSTAGLANDINS
2) Fibrinogen
- Ejaculatory ducts come together to join the urethra within the mass of the ____________.
- Prostate is a single, midline gland just ________ to urinary bladder.
- Prostate is a mass of ____________, glandular tissue, and _____________.
1) prostate gland
2) inferior
3) connective tissue
4) smooth muscle
Prostate gland secretes Prostatic fluid that acts on the _____________ that is inside the seminal fluid that causes the clot in Females Vagina, after the temporery Clotting enzyme, the ____________ will break the clot down.
1) Fibrinogen
2) profibrinolysin
















