I) Introduction to Microeconomics Flashcards
(60 cards)
What is “economy”?
A (large) group of people making decisions.
What is “methodological individualism”?
Individuals behavior => group behavior (economy) Parts => totality
What is “holism”?
Totality => parts Used in sociology
What does mean “formal rigor” in economy?
It means that the models of behaviors are defined mathematically.
What is the function of economy?
f: input → decision/choice
What is the major hypothesis to define “f” (fonction of economy)?
Rationality. Agents are assumed rational.
What does a rational agent?
He always acts in his “best-interest” / according to his preferences.
What is “best-interest”?
Each agent has some well defined preferences (tastes, needs, whims, desires…)
What is “preference”? as a definition
Measure of attractiveness of goods, situations… It is individual tastes and as given.
What is “preference”? mathematically
Ranking all the options in the set of options S.
How do you model a preference?
It is a relation: x≻y. R={(x,y)⎪xRy} (R =relation) This agent prefers x to y. So, he will choose x.
What are the 3 assumptions on preference?
1) x⊁x
2) x≻y => y⊁x
3) transitivity: x≻y, y≻z => x≻z
When is the “choice function” well defined?
If the 3 assumptions are true (preferences are consistent) and if people is rational. The choice function is well defined.
How do you write the “choice function”?
c:S →2ˢ = {set of all subsets of S} X⟼c(X) = {x∈X⎥∄y≻x}
How do you write a “weak preference”?
x≿y x is preferred or equivalent to y.
How do you write an “indifference”?
x∼y
What are the conditions for indifference?
x∼y if and only if: 1) a≿b 2) b≿a Indifference is different from an indecision.
What is “completeness”?
∀ (x,y)∈S, x≿y ∨ y≿x The hard choice doesn’t really exists. It is the fact that the agent didn’t make up his mind.
How do you write a “bundle”?
{qx, qy…} q: quantity I want to buy.
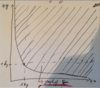
How do you describe a bettering graph?
{(q’x, q’y)⎪(q’x, q’y) ≻ (1,1)}
What is monotonicity?
if: qx>q’x ∧ qy ≥ q’y => (qx, qy) ≻ (q’x, q’y) More is better.
What is convexity of preferences?
If (x,y)∈X, any point in the middle belongs to X.
How is written the “graph of preferences”?
{(qx, qy)⎪(qx, qy)≻(1, 1)}
How are written the “dominated bundles”?
{(qx, qy)⎪(1, 1) ≻ (qx, qy)}