Intestine I U6L04 Flashcards
(126 cards)
how long is the duodenum?
first 11 inches

what seperates the duodenum from the jejunum?
ligament of Treitz.
The jejunum is ____ feet long, and is defined as the proximal 2/5 of the small intestine.
8
The ileum is ___ feet long, and is defined as the distal 3/5 of the small intestine
12
surface area of jejnum compared to ileium?
jejunum has 3x more surface area than the ileum
greater absoprtion occurs in the jejunum or ileum?>
jejjunum

how is increased surface area achieved in the GI system?
successive folding of the surface
The surface area of the small intestine is amplified at three levels:
(1) macroscopic folds of Kerckring
(2) microscopic villi and crypts of Lieberkuhn
(3) submicroscopic microvilli.
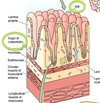
The surface area of the large intestine is amplified at three levels:
(1) macroscopic semilunar folds
(2) crypts (but not villi)
(3) microvilli

average length of the small intestine is
21 FEET
average increase due to mucusal folds?
average increase due to villi?
average increase due to microvilli?
mucosal folds – x 5
villi – x 10
microvilli – x 120
total absorptive surface area of the small intestine is 700 square memters or x ___ in size
x 1000
about ___ of the absorptive surface area is required for absorption.
what is the clinical implication for this?
half the absorptive surface area
half of the absorptive surface area can be surgically removed without compromising absorptive function
celiac disease is associated with a ____ in absorptive surface area
celiac disease is associated with a decrease in absorptive surface area
celiac disease is associated with a decrease in absorptive surface area due to a reduction in the
number and size of microvilli
Sprue is a type of malabsorption syndrome caused by sensitivity to___
gluten
Effect of gluten on small intestine? (2)
Gluten in bread by some means destroys absorptive cells and decreases the number of villi
what is Tropical sprue?
infectious disease associated with diarrhea, malapsprtion, and nutritional deficiencies
where are cells generated in the small intestine? where do they go?
. 1. Cells are constantly being generated at the base of the villi
- then migrate toward the tip, where they are extruded 3-8 days later.

how long are the cells of the intestinal mucosa replaced?
every week
goblet cells secrete protective mucous when stimulated by
acetylcholine
what happens to old extruded cells of the intestinal epithelium
extruded cells are digested in the gut, and their useful contents are recycled
what reduce the rate of cell renewal in the intestinal epithelium? (3)
radiation, malnutrition, or sprue.
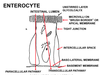
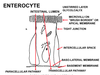
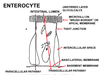
The villi are comprised of absorptive cells called ____,
these are columnar epithelial cells in a single layer.
enterocytes