Intro to Brain Anatomy-Lateral View Flashcards
(68 cards)
Central Nervous System
CNS
Composed of the brain and the spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
PNS
Composed of all parts of the nervous system outside of the brain and the spinal cord.
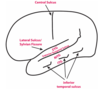
Name the places pointed in red

A) Cerebrum
B) Hypothalamus
C) Corpus Callosum
D) Thalamus

What are the anatomical orientations?
- Anterior = rostral
- Posterior = caudal
- Superior = dorsal
- Inferior = ventral
and
- lateral = towards the side
- medial = towards the midline
Place the orientations in the following image:


Name the different ways to “slice” the brain
- Sagittal
- Coronal
- Horizontal/Axial
What does Sagittal mean?
You cut the brain following the natural division of the hemispheres.

What does coronal mean?
You cut the brain along the x-axis where the x-axis goes from the anterior (front) part of the brain to the posterior (back) of the brain.

What does horizontal/axial mean?
You cut the brain along the y-axis so from ventral (inferior) to dorsal (superior) part of the brain.

Cerebrum
Voluntary movements, sensations, learning, remembering, thinking, emotion, consciousness.
Surface: Cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
Control of hunger, thirst, temperature and other visceral and bodily functions.
Corpus Callosum
Band of fibres connecting the two hemispheres.
Thalamus
Relay station to cortex for sensory information.
Name the parts of the neuron and what they do.

Who discovered the neuron?
Ramon y Cajal
Name the two components of the brain and give a short description.
Grey matter: It is grey because of the density of the cell bodies of the neurons.
White matter: It is white because of the myelin sheath that covers the axons of the neurons.
Myelin Sheath
Fatty substance to enhance conduction of electrical signal down the axon.
True or False
You have myelin in the grey matter.
False, there are axons in the grey matter but they are so small that they do not need the myelin sheath.
True or False
Dendrites are part of the white matter.
False
Components of the grey matter
-
Cerebral cortex:
- Seat of higher cognitive processes
-
Subcortical Structures:
- More primitive controls
- breathing
- heart rate
- alertness
- etc…
- More primitive controls

Cerebral Cortex
- Continuous sheet of tissue
- not homogenous
- cytoarchitectonic areas
- not homogenous
- Has expanded over evolution
- Human cortex is the most convoluted of any primate brain
- Folded into:
- suci
- gyri
- fissures
- 2/3 rds of the cortex is hidden within the suci and fissures
- Not random: Consistent patterns across individuals
- Certain sulci or gyri show strong relations to specific functional processes
- They allow you to identify where certain functions take place in the brain
Sulci
Are the valleys that you find in the brain where as fissures are deeper valleys.
Gyri
The hills that you find in the wrinkles of the brain.
How do we map cortical folds?
(before and now)
slides 15 to 17
- 19th century: it was possible to harden the brain with alcohol
- relatively consistent patterns across individuals
- Certain correlations with functional processes
- Post-mortem
- Surface analysis and restricted sample size
- Today:
- Neuroimaging tools
- many subjects
- 3D
- MRI
- sulcus on the surface of the cortex to its depth
- Petrides lab
- Neuroimaging tools