Knee and Thigh Flashcards
(72 cards)
label this femur

describe the condyles of the distal femur and what they articualte with
the medial is larger than the lateral because it bears more weight in the standing position, since the centre of mass passes medial to the knee joint
lateral condyle is more prominent
the inferior and posterior condyles articualte with the menisci of the knee and tibia
whats this groove called adn what does it articulate with

patellofemoral groove or trochlear goove
articualtes with the patella
whats the function and feature of the lateral condyle
it is more prominent and prevent slateral displacement of the patella during patellar tracking.
people with a more (less prominent) lateral condyle are more likely to experience what
patellar instability
lateral displacement
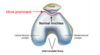
describe the epiconyles
they orginate arebone bony elevations above the non-articular ares of the condyles
medial epicondyle is larger than the lateral one
they are attatchment centres for collateral ligaements
what are the collateral ligaments ?
O and I ?
which is stronger
medial collateral ligament
- O= medial epicondyle of the femur
- I= medial condyle of the tibia
lateral collateral ligaement
- O= lateral epicondyle of the femur
- I= depression on the lateral surface of the fibular head
MCL isbroader butwaker than LCL, which in itself is weak when working in asolation but strong when working together with the arcuate ligament and popliteal tendon

functionof the collateral ligaments
MCL= resists lateral (valgus) angulation of the tibia on the femur
LCL = resists varus angulation of the tibia on the femur
which collateral ligament is stronger
LCL but it is itself weak when in isolation but strong when it works with the arcuate ligaemtn and popliteal tendon
describe the patella
sits within the trochlear groove (patellofemoral groove) of femur
superiorly articulates with the quadriceps tendon
inferiorly articulates with the patellar ligament
- the apex connects with the tibial tuberosity by patellar ligament
- whilst the base forms superior aspect of the bone and provides the insertion area for the quadricpes tendon
- 2 facets;
- medial and lateral
describe the facets of the patella
both the posteriorsurface of the patella articulate with the femur
- medial ; articulates with the medial condyle
- lateral ; articulate with lateral condyle
functions of the patella
- enable the quadriceps muscle to directly cross the anterior aspect of knee as it acts a fulcrum, the patella enhances the leverage that the quadricprs tendon an xert on the femur, increasing the mechanical efficacy of muscle by 30-55%
whats the tibia adn describe it?
the shin bone
articulates with the knee and ankle joints, second largest bone in the body
proximal tibia is widened by medial and lateral condyles wc help with weith bearing
label this


whats special about the condyles of tibia
they forma flat surface known as tibial plateau wc articualtes with femoral condyles to form the major articulation of the knee joint
between the condyles is the intercondylar area and in the centre of that is teh intercondylar eminence
describe the fibula
head of fibula articualtes withthe proximal tibia in the tibiofibular joint and doesnt form the knee joint
distal end widens to assits with weigth bearing
medial mallelous is bony projection infeirorly on medial aspect of tibia and articualtes ith tarsal bones to form part of the ankle joint,
lateraly theres a notch called the finular notch, where the fibular is bound to the tibia forming the inferior tibiofibular joint
whats the intercondylar space
space between the two tibular condyles
at the centre is the intercondylar eminence and on either side of this emence is the lateral and medial intercondylar tubercules
these lateral and medial intercondylar tubercules of the tibia articulate with the intercondylar fossa of the femur
whats special about the intercndylar eminence
attacthment for the cruiate ligaments nd menisci of the knee joint
describe the attatchment for the cruiate ligaments
the posterior cruiate ligaments attatches from the posterior edge of the intercondylar area
describe the tibia shaft
3 borders; anterior posterior and lateral
anterior
- palpable subcutaneously down anterior aspect of leg
- marked by tibial tiberosity - wc is the site of insertion of the patellar ligament
posterior
- marked by ridge known as soleal line, wc is origin of soleus muscle. this line extends inferomedial and blends in with rdge of medial edge of tibia
lateral
- aka interosseous boader and gives attatchemnt to the interosseous membrane that binds the tibia and the fibula together
describe the distal fibular
tibia widesn to assist with weigth bearing
medial condyle extends inferiorly to form the medial malleous wc articulats with the tarsal bones to form the ankle joint
laterally theres a fibular nothc wc articulates where fibula is bound to tibia and forms the inferior tibiofibular joint
describe the fibula
localated on the lateral aspect of the lef adn acts as a mucle attatchment
3 main articualtion :
distal tibiofibular jont (arituclates with teh tibia at the fibular notch
proxial tibiofibular joint (articulates witht eh alteral condyle of the tibia
ankle joint (articltes with the talus bones of the foot
whats special about nerves and the fibula
the common peroneal (common fibular) nerve winds around the posterior and lateralneck of the fibular and so is vulnerable to damage in proximal fibular fracture
descrube the boarders of the fibula
laeral
anteiror and postierior














