Knee, Ankle, and Foot Tests Flashcards
(16 cards)
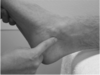
Patellar Apprehension Test
Pt supine, legs straight, quads relaxed. Apply firm, slow, gentle pressure pushing the patella laterally, then medially. Observe for patient apprehension.
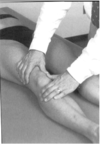
Functional Tests and Knee Resistance
Have patient squat or step-up (wt bearing movements). Knee resistance: pt seated, place one hand on the quads, the other the ankle, have pt extend knee while examiner applies resistance.

Valgus Stress Test
Pt is supine, legs straight. Knee in neutral (0 deg). Stabilize medial ankle and apply a lateral-to-medial force as the lateral knee . Repeat with knee at 30 deg flexion (can achieve this by bringing leg off table).
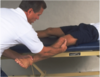
Varus Stress Test
Pt is supine, legs straight. Knee in neutral (0 deg). Stabilize the lateral ankle and apple and medial-to-lateral force at the medial knee. Repeat test with knee at 30 deg flexion.
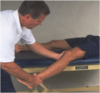
Anterior Drawer Test, Knee
Patient is supine, knee flexed to 90 deg, foot on the table. Stabilize pts leg by sitting on dorsum of foot and place hands behind the proximal tibia. Pull tibia anteriorly (towards you) trying to displace it forward). ACL should stop the movement
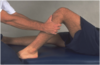
Posterior Drawer Test, Knee
Patient is supine, knee flexed to 90 deg, foot on the table. Stabilize pts leg by sitting on dorsum of foot and place hands on anterior proximal tibia. Push on the tibia posteriorly

Lachman’s Anterior and Posterior Test
Patient is supine, knee flexed to 30 deg. Anterior Test: Stabilize fever with one hand and pull the tibia anteriorly with the other hand. Posterior: stablize the femur with one hand and push the tibia posteriorly with the other hand.
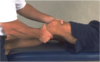
Thessaly
Patient performs test on unaffected side first. Patient stands flat footed on one leg with knee in neutral first, then, if no positive, knee flexed 20 deg while examiner helps pt balance. Pt then rotates the femur on the tibia internally and externally three times while maintaining knee flexion.

Ege’s Test
patient standing, feet 10-15 inches apart. Medial meniscus: fully external rotation of legs with slow squate (like a ballet plie). Lateral meniscus: full internal roation of legs with legs with slow squat.

Anterior Drawer Test, Foot
Pt is supine or seated. Place one hand on the anterior tibia and the other hand on the posterior calcaneus. Pull the foot anteriorly. Observe for excess movement and/or pain, popping. Perform in neutral position (90 deg), plantar flexion (20 deg).
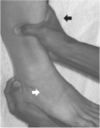
Posterior Drawer Test, Foot
Pt seated, foot on table. Stabilize dorsume of the foot with one hand and grip the posterior tibia with the other hand. Pull the tibia anteriorly. Observe for ligament laxity. Perform in neutral (90 deg).

Kleiger’s Rotational Stress Test
Pt supine. Stabilize tibia with one hand and rotate the foot laterally (not eversion)–like you are rotating a door knob. Observe for excess movement, pain and/or popping.

Talar Tilt Test
Pt supine. Stabilize tibia with one hand and invert the foot with the other hand. Repeat test with eversion. Observe for ligamentous laxity.

Thompson Test
Pt prone. Squeeze the calf at its widest point and observe for the presence of plantar flexion with the calf squeeze. Observe for plantar flexion of the ankle. (Torn achilles = no flexion)

Morton’s Test
Patient is supine or seated. Squeeze the foot around metatarsal heads. Observe for foot pain or discomfort.

Tinel’s Test, Ankle
Pt prone, supine or seated. Percuss over the medial ankle behind medial malleolus in the tarsal tunnel (posterior tibial nerve). Percuss over the dorsum of the foot lateral to the tibialis anterior tendon (deep fibular nerve). Observe for pain, tingling, paresthesia, electrical sensations.