L7 - Pelvis & Perineum Flashcards
(72 cards)
The pelvic cavity is continuous with the abdominal cavity and divided into two regions
Name them and their contents:
False [greater] pelvis
- superior region related to upper parts of the pelvic bones
- generally considered part of the abdominal cavity
True [lesser] pelvis
- inferior parts of the pelvic bones, sacrum, and coccyx
- has an inlet and an outlet

What is the area inferior to the pelvic inlet?
A. True Pelvis
B. False Pelvis
A. True Pelvis

The Pelvis
- Pelvic inlet
- Pelvic walls (2 muscles)
- Pelvic floor (diaphragm)
- Pelvic Outlet (orfices coming out of pelvic diaphragm)
Contain Elements of the:
- urinary
- gastrointestinal
- reproductive systems
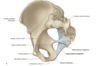
Name the Pelvic Bones
- Ilium
- Ischium
- Pubis
Converge into acetabulum (femur articulates there)
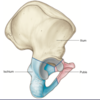
Name the purple starred structures

ASIS
Ischial Spine
Ischial Tuberosity

What is the sacral promontory?
In between the 5th lumbar and 1st sacral vertebrae
- More prominent in males

Where do the spinal nerves of the sacrum come out of?
Anterior sacral foramina
Posterior sacral foramina

What connects the sacrum to the L5?
zygapophysial joints
- connects adjacent vertebrae
- specifically between the L5 and the sacrum
Joints
- zygapophysial joints
- Sacro-iliac joints

Name the main ligaments of the pelvis
Main ligaments:
- Anterior Sacro Illiac ligament
- Lumbosacral ligament
- Iliolumbar ligament

What is the common site of fractures,
also known as
the weakest point in the pelvis
Superior/Inferior Pubic Ramus
Superior/Inferior Ischial Ramus
= Ishiopubic Ramus

Name the differences between women and men
pelvis size, shape, and projections
Female:
- Pelvic inlet is more circular
- Wider infrapubic angle (80-85 degrees)
- Less prominent Ischial Spine
- Less prominent Promontory
Male:
- Pelvic inlet is narrower and heart-shaped
- Narrower infrapubic angle (50-60 degrees)
- More prominent Ischial Spine
- Prominent Promontory (sacral promontory)

The pelvic inlet contains 5 structures, name them
PAAPP
- Promontory of sacrum
- Ala of sacrum
- Linea terminalis [Arcuate line]
- Pecten pubis/pectineal line
- Symphysis pubis

All of the following are a part of the linea terminalis EXCEPT:
A. Pubic Crest
B. Arcuate Line
C. Pectin Pubis
D. Ala of sacrum
D. Ala of sacrum
Linea terminalis = Arcuate line, Pecten pubis, Pubis crest
What are the contents of the Pelvic Wall?
- Sacrum (bone)
- Coccyx (bone)
- Piriformis (muscle)
- Obturator Internus (muscle)
- Sacrospinous Ligament & Sacrotuberous Ligament
- Pelvic bones inferior to linea terminalis

What are the ligaments that form the pelvic wall?
Sacrospinous Ligament:
- Sacrum to the ischial spine
Sacrotuberous Ligament:
- Sacrum to the ischial tuberosity
These ligaments stabilize the sacrum on the pelvic bones by resisting the upward tilting of the inferior aspect of the sacrum

What are the muscles that make up the pelvic wall?
Piriformis
- Piriformis goes through the GSF
Obturator internus
- Obturator Internus goes through the LSF
Both:
- External Rotators
- medial surface of greater trochanter of femur

How many Apertures are in the pelvic wall and what are they?
Three major apertures:
- the obturator canal
- Greater sciatic foramen
- Lesser sciatic foramen
Obturator canal –> obtrurator vessels
GSF –> Piriformis
LSF –> Obturator internus
What is the name of the following structure in green?
A. Promontory of Sacrum
B. Pubic Crest
C. Pectin Pubis
D. Arcuate Line
E. Margin of Ala

D. Arcuate Line

True or False
The superior gluteal nerve and vessels are inferior to the piriformis
False
The superior gluteal nerve and vessels are superior to the piriformis

Structures in relation to the Piriformis
Superior:
Superior Gluteal Nerve, Artery & Vein
Inferior:
Sciatic Nerve, Inferior Gluteal Nerve & Internal Pudendal Vessels
True or False
Obturator Vessels run through the obturator canal
True
Name the structure in green
A. Ischial Tuberosity
B. Ischial Spine
C. AIIS
D. PIIS

B. Ischial Spine

What is the Pelvic floor formed by?
- Pelvic diaphragm
- Perineal membrane
- Deep perineal pouch
The pelvic floor separates the pelvic cavity, above, from the perineum, below.

The pelvic diaphragm
Formed by funned shape muscles
Levator anni
- Contributes to the formation of the pelvic floor
which supports the pelvic viscera
- Maintains _90-degre_e angle between the rectum and anal canal
- Reinforces the external anal sphincter and, in women, functions as a vaginal sphincter
Coccygeus muscle
(not in levator anni)
- supports the pelvic viscera
- pulls coccyx forward after defecation





































