Lab Exam Flashcards
(142 cards)
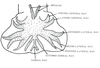
Primates

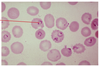
Entamoeba histolytica
Ameoba pathogenic to primates
Infection in liver and brain can be fatal
Four (4) nuclei is diagnostic
Human

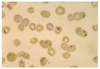
Entamoeba coli
Eight nuclei
Larger size than E. histolytica
NON-pathogenic
All animals + humans

Naegleria fowleri
Large dark nuclear endosome is diagnostic
Brain infection from swimming in hot water
Infects all animals + humans
Animals + humans

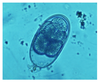
Giardia sp.
Trophozoite stage (rare in feces)
Tear drop shap and two nuclei
Remember zinc sulfate soolution
Animals + humans

Giardia sp.
Cyst stage
Four nuclei (only 3 may be visible)
More common in feces
Cattle

Trichomonas foetus
Undulating membrane is diagnostic
Direct smear of preputial wash from bull
Causes abortions in cattle
Chickens & turkeys
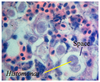
Histomonas meleagridis
Round parasite with central nuclei
Large space between parasite and host = diagnostic
Infects turkeys
Heterakis is a transport host (nematode)
Swine and humans

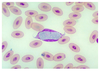
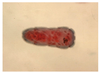
Balantidium coli
Trophozoite stage
Harmelss commensal of swine intestine
Pathogenic in humans (primates)
Pear shaped
Macro and micro nulcei plus cilia
Swine and humans
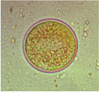
Balantidium coli
Cyst stage
Fish

Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
Trophozoite stage
Horse-shoe macromucleus
“White spot” in fish
T. stage lives in galleries in the epithelium
Fish

Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
Infective stage = tomite or swarmer
Red stained both macro and micro nucleui
Rabbits
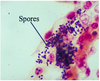
Nosema cuniculi
Dark stainging spores!
Gram positive staining
Infects rabbits
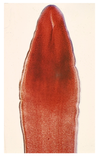
Chickens
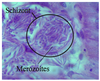
Eimeria tenella
Major coccida of chickens
Infection of cecum
Note: Schizonts containing merozoites (bananas)
Chickens

Eimeria tenella
Chicken cecum
Note: bloody casts
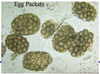
Cattle

Eimeria bovis
Left: unsporulated oocyst
Right: sporulated oocyst
4 sporocysts with 2 sporozoites each
Highly pathogenic bovine coccidia
Goose kidney
Coccida

Eimeria truncata
Infects goose kidney
Ocysts in urine!
Rabbits

Eimeria stiedai
Infects rabbits
Swine
Coccidia
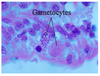
Isospora suis
Most pathogenic coccida of swine
2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites each!
Eimeria versus Isospora
Eimeria: cattle and poultry
4/2
4 sporocysts with 2 sporozoites each
Isospora: dogs and cats
2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites each
Swine and humans = both are infective
Mouse abdominal fluid

Toxoplasma gondii
Motile tachyzoites
DH: cat
Mouse brain

Toxoplasma gondii
Cyst with bradyzoites
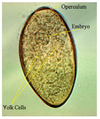
Duck muscle

Sarcocystis sp.
Rice grains in muscle = sarcocysts
Duck is IH
DH are carnivores
Thin walled sporulated sporocyst in fecal float
All mammals
DMSO carbol fuschin stain
Cryptosporidium parvum
Pink stained oocysts
Small oocysts
4-8 naked sporozoites in fresh feces = NO sporocyst
Does not need to sporulated to be infective
All mammals

Cryptosporidium parvum
Oocysts on villi of small intestine