Lab Normals Flashcards
Learn the normal lab values (53 cards)
Normal WBC count
4.0 - 10.5 x10^3/ul
Normal lymphocyte pecentage
14 - 46%
normal neutrophil percentage
40 - 74%
normal absolute lymphocytes
0.7 - 4.5 x10^3/uL
normal absolute neutrophils
1.8 - 7.8 x10^3/uL (1500 - 8000)
normal monocyte percentage
4 - 13%
normal eosinophil percentage
0 - 7%
normal basophil percentage
0 - 3%
What does erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) measure?
a measure of inflammation, how quickly the RBCs settle to the bottom of a test tube
What is the dx of increased WBC?
leukocytosis
What is the dx of decreased WBC?
leukopenia
normal absolute eosinophils?
0 - 600
normal absolute basophils?
0 - 200
normal absolute monocytes?
0 - 800
normal absolute lymphocytes?
1000 - 4500
Describe a neutrophil’s appearance
multilobed, purple nucleus, light purple granulomas, pink plasma
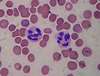
Describe an eosinophil’s appearance
bilobar nucleus, red granulocytes, red plasma

Describe a basophil’s appearance?
unilobar, large purple granulomas that take up most of the cell, purple plasma

Describe a monocyte’s appearance
Large purple nucleus sometimes horseshoe shaped, fine granules, blue/gray/purple cytoplasm

Describe a lymphocyte’s appearance
Large purple nucleus takes up circumference of cell, small cell the size of a RBC, no granules

Which cells are considered phagocytes? (4)
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes
What are potential causes of lymphocytosis?
infection, leukemia, lymphoma
What are potential causes of lymphocytopenia?
acquired or inherited immunodeficiency, chemo or radiation induced destruction of lymphocytes
Locations of adult red bone marrow (6)
pelvic bone, ribs, proximal portion of the humerus/femur, cranium, vertebra, sternum