lab practical 1 Flashcards
(66 cards)
fungi reproduce…
asexually
the three shapes of bacterial cell walls
bacillus (rod-shaped), coccus (spherical) and spirillum (spiral)

penicillium
fungi
phylum: ascomycota
multicellular free-living heterotrophic
appearance: clear rings, sort of square
have one flagellum, most primitive protozoans and are parasitic as well as free-living heterotrophs
flaggellates
Ex. trypanosoma (cause african sleeping sickness)

rhizopus
fungi (bread mold)
phylum: zygomycota
multicellular, free-living, heterotrophic
Reproducing: bulbs with stems on two ends mass: fuzzy with dots
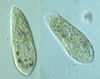
paramecium
protist
phylum: cilophora
unicellular, free-living, heterotrophic, protozoan
Swimmy when alive, ovals w/ distinct nucleus looking inside circle
How large is a tryanosome relative to Amoeba?
Much smaller
Archaebacteria that are survivors of ancient lines that have persisted in habitats similar to those present when bacteria first evolved
extremophiles
pigments of cyanobacteria
chlorophyll a, phycocyanin an phyocoerythrin
Free-living in freshwater. One of the most studied and undergoes reproduction through conjugation.
paramecium (ciliate)
segmention of the body for reproduction
transverse fission
derive their energy from photosynthesis or the oxidation of inorganic molecules
autotrophic
The three main domains of organisms
Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya
Eukaryotes
has membrane-bound organelles

saccharomyces
fungi (yeast)
phylum: ascomycota
unicellular, free-living, heterotrophic
appearance: little purple/pink circles
slime mold that live alongg the damp forest floor in a mass of brightly colored protoplasm
plasmodium
when do fungi reproduce sexually?
When hyphae of two genetically different individuals of the same species encounter one another.

amoeba
protist
phylum: rhizopoda
unicellular, free-living, heterotrophic, protozoan
appearance: spongebob background clouds with center dot
Stains pink
Gram Negative
when fungi’s nuclei fuse
karyogamy
How do daughter colonies exit Volvox?
They are released when the parent cell disintegrates
Prokaryotes
lacks cell membrane bound organelles,
four major phyla of fungi
chytridiomycota, zygomycota, ascomycota and basidiomycota

volvox
protist
phylum: chlorophyta
unicellular, free-living, autotrophic, algae
appearance: orbs with little orbs in them
















