Lameness Flashcards
(82 cards)
What can you add to a ruminants diet if high grain diets to rebalance high P: CaCO3?
Calcium carbonate (limestone)– immediately for growing ruminants, if > 8 weeks full feeding for adults
High serum phosphate from a diet high in cereal grains in growing cattle and sheep does what?
Antagonises serum Ca2+–> Low Ca2+ stimulates PTH–> Ca resorbed from the bone–> tends to cause osteoporosis in sheep and cattle
How can we assess secondary nutritional hyperparathyroidism?
* Urinary P excretion… compare urein: serum % of phosphorous and creatinine (baseline metabolite that the kidney doesn’t reabsorb)

What can happen with low dietary vitamin D?
Vitamin D needed for active Ca & P absorption from gut–> low Ca &/0r P means bone can’t be mineralised–> Rickets in growing animals or Osteomalacia in adults (remodelled bone is soft)

How do you ensure enough vitamin D in a ruminants diet?
Avoid rachitogenic factors (anti vit D) and high NH4 (antagonises dietary Ca absorption) e.g. in oat crops
** can give oral or injectable supplements in young sheep if signs are developing to help in situations of Ca deficiency
* Vit D toxicity causes abnormal tissue mineralization
Keys in a ruminants diet?
* Enough energy, protein, Ca, sunlight, Cu
* Parasitism can have a big effect
* Ca: P balance especially with cereal supplements
How much calcium do you need to add to a diet to fix Ca:P ratio?

How can nutrition affect lameness?

90-90-90 rule?
90% of a herd’s lameness from the feet
90% of those lamenesses are in the back feet
90% lateral claw

Most cattle lameness from what lesions?

Economic losses due to?

Approximate cost of lameness in an individual treatment
$200 per lame cow (1998) in AUS

Average loss of production in a lame cow?

Lameness and reproductive performance?

What percentage of cows that are culled are culled for lameness?

Multifactorial aetiology of lameness in cattle

Predisposing causes of lameness
* Infectious agents- Fusobacterium necrophorum
* Nutrition- rumen acidosis and laminitis
* Hereditary- e.g. cork screw claw, sore ulcer
* most lameness due to over-worn, bruised soles or stones in interdigital cleft
* Increased when farm track had steep slope, course gravel or broken sections
* Bail feeding associated lower incidence lameness
* Cows should not be hurried on farm tracks
** Risk factors on track
- below avg track maintenance, bad cow flow on track (number of congestion points), patience of farmer- motor bikes, biting dogs
**Risk factors in shed
- biting dog, contentment of cows, cow density in yard, aggressive use of backing gate
** Risk factors in animals
- higher Friesians, white feet

Lameness prevalence picture

Examination of the lame cow
* Observe standing free in yard
* History- how long lame, treatment?
* Clean with scrubbing brush, water… hoof knife, rasp or angle grinder
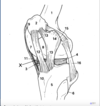
* Look for swelling at the coronary band
* look for defects or penetrations of the sole
* Use hoof testers to check for pain
* Examine for axial, abaxial wall cracks
* Thoroughly explore any defects detected
8 point exam
- Which leg is the cow lame in?
- Is the leg swollen and obviously painful above the hoof?
- Are cracks present in external surface of the hoof wall of lame leg?
- Is there soft tissue swelling with foul swelling discharge and dead and damaged skin in the interdigital space?
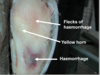
- Is there abnormal discolouration in the sole horn? Do not confuse with normal pigment (usually black)
- White line- expanded and filled with mud and gravel especially towards heel area?
- Are there any sensitive areas which cause withdrawal reflex?
- Seek vet advice OR withdrawal response detected– bruising- rest; toe/foot abscess or under run sole- trim, pare, grind until loose sole horn removed back to normal horn; pus detected- establish drainage
How do you lift the hind foot? What is a good idea if there is hindfoot lameness?
* possibly low dose Xylazine with hindfoot

How do you lift the front foot?
* Loop around leg at level of dewclaws
* over rail and back under axilla
* then back over rail and lift

What’s the difference between Holstein and Friesian?
Holstein Friesians are a mixture
Holstein are bigger girls– genes from North America
Friesian gene is from Europe
** our herds are a mixture of the two so a middle size