Lec 11- Liposomes (part 2) Flashcards
Reaching tumour sites
- Avoid MPS uptake
- Long circulating
- Escape the circulation
3 commercial liposome formulations of anthracyclines
Myocet
- These are liposomes of 180nm in size entrapping doxorubicin
- They are composed of egg phosphatidylcholine and ChE (55:45mol %) so fit within the classical liposomes category
- Due to their size, the liposomes are rapidly taken up by the MPS
- This avoids peak plasma levels and reduces toxicity
- The liposomes cleared by the MPS are then thought to create an ‘MPS Depot’ from which drug re-enters the bloodstream mimicking a slow infusion
- As a result tissue concentrations are comparable to the same dose of doxorubicin HCl
- The recommended dosage is 60-75mg/m2 every 3 weeks
3 commercial liposome formulations of anthracyclines
Caelyx
- This contains doxorubicin entrapped within liposomes 80-100nm in size
- The liposomes are composed of hydrogenated phosphatidylcholine, cholesterol, PEG2000-distearoyl phosphatidylethanolamine, α-tocopherol (56:38:5:0.2 mol %)
- The PEG2000 coating gives the liposomes the stealth properties and the a-tocopherol is used as an anti-oxidant in the formulation
- This formulation is used for the treatment of solid tumours including Kaposi sarcoma and ovarian cancer
- It is supplied as a sterile, red liposomal dispersion and must be diluted in 250mL of 5% dextrose prior to administration

DaunoXome
- These liposomes are composed of DSPC: ChE (2:1 mol ratio) and have a diameter of 45nm with entrapped daunorubicin
- DaunoXome is indicated for the treatment of advanced HIV-related Kaposi sarcoma
- It is available in a single-use vial for IV infusion and the liposome dispersion should appear red and translucent
- The liposome formulation helps to selectively target the daunorubicin to solid tumours
- Whilst this is not a stealth formulation tumour targeting is still noted with this formulation presumably due to the high transition temperature lipids used (DSPC) and the small vesicle size which helps pro-long blood residence time
Surface engineering of the liposomes
- MPS recognises charged surfaces on particulates avoid by formulated as a neutral surface
- MPS recognised tagged or opsonised surfaces
- PEG coating prevents opsonisation due to steric hindrance

Stealth tactics
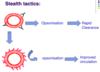
Why do we need long circulation
- Enhanced circulation allows the liposomes to target tumour sites
- This is due to the unique blood vasculature with tumour
- Blood vessels in growing tumours are leaky to circulatory macromolecules and large particles
- Allowing them easy access to the tumour’s interior
Why do we need stealth tactics
- Liposomes can be recognised as foreign bodies
- They are filtered out by the liver and spleen
- The immune system recognises and destroys liposomes
- This is through a method known as opsonization
PK data
- Non-modified = saturable because there is binding to a receptor
- Stealth no binding so will be removed when kidney/liver
*
- Stealth no binding so will be removed when kidney/liver

Clearance of liposomes

Liver and spleen uptake
- Starts off fast and then plateau due to saturation
- Stealth = natural removal (kidney/liver)/ Removal is independent on concentration

Passive targeting to tumour sites: The EPR effect
- Lower permeability of the blood vessel prevents the drug from escaping to area’s where it is not needed
- The high permeability of the blood vessel in the tumour site allows liposomes to escape
- Tumour tissue- the tumour tissue has poor lymphatic drainage, trapping the liposome in the cancerous tissue
- Liposome entrapped drug
The localisation of doxorubicin in AIDS-KS lesions

Liposomes bring with them new side-effects
- Hand-foot syndrome (Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia or PPE)
- Redness, swelling and sores on the palms of your hands and soles of your feet
- Reports of 48% with Caelyx v 2% with drug
Counselling
- To minimise
- 4-7 days after each infusion, keep hands and feet uncovered (Avoids socks/gloves/tight-fitting shoes) and soaking them in cool water when possible
- Avoid exposing the skin to very hot water e.g. saunas and jacuzzis and avoid exercise that might cause damage to the skin e.g. jogging
Liposome-based products
*

Trigger-release liposome formulations: thermodox
- Heat tumour
- Liposome reaches transition temperature- gel-like structure= increased release of drug

Visudyne: Photosensitizing agent
- Vertoporfin (drug)
- Egg phosphatidylglycerol
- Dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine
- Ascorbyl palmitate
- Butylated hydroxytoluene
Role of liposomes in Visudyne
- Vereportin is hydrophobic and self-aggregates
- This severely limits drug bioavailability
- Maintains vertporfin in monomeric form increasing bioavailability

Treatment of age relatedmacular degeneration
- Scarring of eye tissue
- Production of faulty/leaky blood vessels

Applications
- Laser enhances the release of drug by increasing flexibility of liposome membrane

Liposomes as vaccines
- Virosomes are small vesicle structures, ~150nm in size, prepared from the outer coat of influenza virus and additional phospholipids
- Epaxal: This is a hepatitis A vaccine containing inactivated hepatitis A virus. The inactivated virus has been adsorbed onto virosomes
Summary: drug delivery using lipid systems
- DNA delivery
- Delivery of vaccines
- Pressure probes
- Photo-sensitive liposomes
- Enhances solubility
Summary
- Liposomes currently provide the ability to passively target encapsulated drugs to specific sites of disease
- This allows liposomes to improve the therapeutic index of several drugs
- However,
- alternative side-effects do arise from the use of liposomes


