LEC 9: Histology of the Nervous System - 08.22.14 Flashcards
(43 cards)
From which embryological structure does the CNS develop and what does it include
- develops from neural tube
- Includes:
- brain (cerebrum and brainstem)
- spinal cord
From which embryological structure does the PNS develop and what does it include
- neural crest derivative
- includes:
- spinal (sensory and motor) nerves
- sensory ganglia
- Schwann cells
- Autonomic nervous system
- sympathetic
- parasympathetic
- enteric
What are the two (2) main parts of the brain

- cerebrum
- brainstem
What are the three (3) layers of meninges covering the CNS
- Dura mater
* tough, fibrous, protects brain inside skull - Arachnoid mater
- arachnoid trabeculae are connective tissue channels that connect arachnoid and pia
- blood vessels go through arachnoid
- arachnoid approximates brain surface
- Pia Mater
* follows every nook and cranny of brain
meningiomas
tumors in meninges (pia, arachnoid, dura)
Ventricular System
fluid filled sac that is the internal core of CNS; filled with CSF, which is produced by the choroid plexus

ependymoma
tumors of ependymal cells
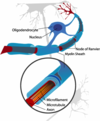
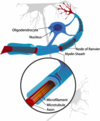
Ciliated ependymal cells
brain ventricles (ventricular system) are lined by ciliated ependymal cells; promote movement of CSF

Four (4) cellular constituents of the CNS
- neurons (nerve cells)
- glia (supporting cells)
- capillaries
- ependymal cells
Parts of a neuron
- one or more dendrites
* information/signal receivers - a cell body (soma)
* metabollic support, sums info received - one axon
* transmits message
Neurons are structurally and functionally polarized
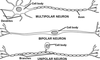
Neuronal subtypes, categorized by relationship between cell body and its processes
- multipolar neurons
* throughout nervous system - bipolar neurons
* only a few places (retina, C8 nerve which controls audio) - unipolar neurons
* found only in sensory ganglia (info coming from skin, muscles, etc.)
Neuronal subtypes, categorized by cell body shape and dendritic process morphology
- pyramidal cells
- spiny stellate cells
Main 2 types of cells of cerebral cortex
Role of spines along axon of pyramidal cells
change with experience, learning, memory, cognition, plasticity, hormones, aging
Neuronal subtypes, categorized on the basis of the axon
- long axon projection neurons
- to other neurons
- to effectors (muscles, glands)
- short axon interneurons
* amacrine cells (interneurons in retina)
functions of cells with short axons (or no axon, as in amacrine cells)
local circuit neurons (e.g. retina)
Two (2) parts of the axonal ending
- telodendron
- terminal boutons

What are the major organelles found in axon terminals
- mitochondria (ATP)
- synaptic vesicles (contain neurotransmitter molecules)
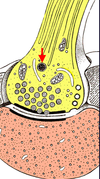
Components of synapses
- presynaptic membrane (with synaptic vesicles)
- synaptic cleft
- postsynaptic membrane
NB: can also have axo-spinous synapses

Neuromuscular Junction
- motor end plate is an enlarged terminal with:
- synaptic vesicles
- junctional folds
- enlarged synaptic cleft
- muscle sole plate
- end plate is covered by lemmocyte cytoplasm and basal lamina

nissl bodies
large glandular body found in neurons; actually RER with rosettes of free ribosomes
NB: spinal cord motor neurons have a prominent nucleus and lots of nissl

Lower motor neuron diseases
- polio
- ALS
Motor neuron diseases
- Parkinson’s disease and related disorders
- Huntington’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias
- Prion disease
- Spinocerebellar ataxia
- Spinal muscular atorphy
Three (3) types of neuronal cell death
- apoptosis (programmed cell death)
- necrosis/cytoplasmic
- authophagy
Glia cells
support cells of neuronal cells