Lecture 13: CNS Histology Flashcards
(53 cards)
What is the name given to support cells in nervous tissue that are involved in conduction speed, repair and NT maintenance?
Glia
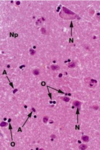
What is a neuropil?
Dense network of interwoven nerve fibers and their branches and synapses, together with glial filaments
What is the distal end of the axon called?
Terminal arborization -> has some branching, collateral branching
Ends of axons usually have small telodendria, what is this?
Dilation of branch ends and contact postsynaptic cell
An electrical synapse permits direct, passive flow of electrical current from one neuron to another, how does the current flow from one neuron to another?
Via gap junctions
The proximal regions of astrocytes are reinforced with intermediate filaments made of what?
Glial fibrillation acid protein (GFAP)
What are the functions of astrocytes?
Helps form BBB Regulates interstitial fluid composition Provides structural support and organization to the CNS Assists with neuronal development Replicates to occupy space of dying neurons
What are the functions of ependymal cells?
Lines ventricles of brain and central canal of SC Assists in production and circulation of CSF
What are the functions of microglial cells?
Phagocytic cells that move through the CNS Protects the CNS by engulfing infectious agents and other potential harmful substances
T/F:Schwann cells are unique in the fact that they will entrap axons from multiple neurons
False -> This is true of oligodendrocytes!
Ependymal cells are _________________ cells that line the fluid-filled ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord
Columnar or cuboidal cells
The apical end of ependymal cells have cilia and long microvili. What is the purpose of these structures?
Facilitate movement of CSF Likely involved in absorption
T/F: Microglia are less numerous than oligodendrocytes or astrocytes
True
What cell type is the major mechanism of immune defense in the CNS, removing any microbial invaders?
Microglia -> they originate from monocytes
The choroid plexus is an elaborately folded and highly vascular tissue, found in the roofs of the 3rd and 4th ventricles, and in parts of lateral venticular walls. It contains a thin layer of ____________________ covered by __________________ cells
Well-vascularized pia mater; cuboidal ependymal cells
The choroid plexus functions to. Remove __________ from blood and releases it as _______
H2O;CSF
Where does the central canal lie in the spinal cord?
In the central commissure of grey matter -> lined by ependymal cells and contains CSF
What types of nerve fibers does the white matter of the spinal cord consist of?
Ascending tracts of sensory fibers and descending motor tracts
The sharply folded cerebellar cortex is organized into 3 layers. What are they?
Molecular layer Purkinje cells Granular layer
What layer of the cerebellar cortex contains various very small, densely packed neurons and little neuropil?
Granular layer
What layer of the cerebellar cortex extends dendrites throughout the molecular layer as a branching basket of nerve fibers?
Purkinje cell layer
What layer of the cerebellar cortex has much neuropil and scattered neuronal cell bodies?
Molecular layer
The neocortex of the cerebral cortex has a variety of cells, divided into 5 different morphological types. What are they?
Pyramidal cells Stellate (granule) cells Cells of martinotti Fusiform cells Horizontal cells of Cajal
What cell type found in the cerebral cortex are small and spindle shaped but oriented paralllel to the surface and are the least common?
Horizontal cells of Cajal