lecture 26: breast and cancer stem cells Flashcards
(47 cards)
What defines stem cells?
- defined by their ability to self-renew and differentiate along multiple lineages
- stem cell → common progenitor → committed progenitor → mature cells
- stem cell → stem cell

What is development of the breast?
- newborn → puberty → pregnancy → lactation → involution (→ pregnancy → etc)
- proliferation at puberty
- proliferation and differentition during pregnancy
- differentiation during lactation
- apoptosis during involution

What are the three distinct epitheli cell types seen in breast?
- 18 day pregnant
- luminal epithelium
- alveolar
- ductal
- myoepithelium

For what are mammary stem cells required?
- homeostasis in the mammary gland and growth during pregnancy
- remarkable generative capacity of breast tissue
- more than 25-fold expansion of breast ‘epithelium’

How have in vivo strategies been used to define the mammary stem cell (MaSC)?
- identification of cell surface markers to allow fractionation of mammary cells by flow cytometry
- transplantation studies:
- perform limiting dilution assays to allow comparison of the relative repopulating frequencies of different subpopulations
- demonstrate the multilineage differentiation capacity of SCs. Serial transplantation is the ‘gold standard’ to prove the self-renewing capability
- lineage tracing studies in vivo
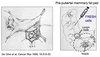
What is in vivo characterization using mammary fat pad transplantation?
- mammary gland not an essential organ
- cauterize in a young animal (3 weeks)
- remove rudimentary tree attached to nippple
- leave behind an intact fat pad
- inject FRESH cells into this
- harvest 8 weeks post-transplantation
- ask whether we see a ductal tree that has emerged in this area
What are the multiple cell types of the mammary gland?
- luminal epithelial cells
- myoepithelial cells
- basement membrane (separates epithelial cells from surrounding stroma)
- fibroblasts
- adipocytes
- blood vessel
- lymph node
- macrophages
- complex microenvironment

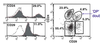
How many epithelial subpopulations were defined by cell surface markers?
- CD24 + or -
- heat stable antigen
- CD29 + or -
- beta1-integrin
- DP - double positive - smallest population, 4.8%
- CD24+/CD29- 23.9%
- double negative = 55.4%
- CD29+/CD24- = 5/3%
- transplant cells in numbers proportional to their frequency in the overall population
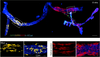
What was transplantation of subsets of lineage-cells?
- cells double-sorted
- rosa 26 donors (lacZ gene in Rosa-26 locus)
- only one population had repopulating capacity when put into cleared fat pad
- CD29hi
- CD24+

Were they able to get generation of a functional mammary gland from a single stem cell?
- yes
- beta-galactosidase makes blue
- capable of multilineage differentiation

Can the Lin-CD24+CD29hi cell self-renew?
- serial transplantation studies
- MaSC
- primary transplantation
- primary outgrowth
- secondary transplantation ( first generation self-renewed MaSCs)
- secondary outgrowth
- tertiary transplantation (second gen self-renewed MaSCs)
- tertiary outgrowth
- most could be passaged ~8 times

Do bipotent cells exist and function in vivo?
- big controversial issue in the field
- they had done research with a team in canada → recapitulated findings independently → found a stem cell that could give rise to all of these cells
- in 2011 a paper appeared and said that bipotent stem cells do not exist - only unipotent cells exists
- there is a myo-SC → myoepithelial cells
- luminal SC → ductal and alveolar cells
- claimed using lineage tracing
- at the same time they were also carrying out lineage tracing experiments

What is 3D imaging of the mammary gland?
- 3 week-old gland prior to puberty
- this is about a 4mm section of an intact mammary gland
- can see elongated myoepithelial cells

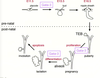
What is the strategy for in vivo lineage tracing?
- Rosa26 is a strong, ubiquitous promoter
- dtTomato is a red fluorescence protein
- all daughter cells of labeled parental cell are permanently marked
- single colour for quantification
- toxicyclin inducible system
- tet operon that contains cre
- third cross where cre induces expression of a promoter gene
- triple transgenic mice
- if the promoter is expressed in a specific cell of interest, in the presence of toxicyclin, it will activate the tet operon → cre mediating recombination → expression of that particular promoter or reporter gene in that particular cell type
- indelible marking of all daughter cells of that parental cell

What is confetti?
- a stochastic multicolour cre reporter for clonality studies
- 4 fluorescent proteins
- if you deliver just a small single pulse of an agent (toxicyclin) → random activation of only one of four colours in that cell
- because only one pulse is delivered not flipping backwards and forwards

What was population dynamics of K5-expressing cells in puberty?
- equi-expression of all four fluorescent proteins
- K5 marks long myoepithelial cells
- shows that many progenitor cells are involved in morphogenesis of the gland during puberty

What were they able to show in the end?
- K5 marks both luminal and myoepithelial cells after induction in the adult
- able to show that after an 8 week chase
- unicoloured clonal regions
- both myoepithelial and cuboidal luminal
- proved that bipotent stem cells exist
- capable of giving rise to all the epithelial cells of the mammary gland
- also luminal progenitor cell exists
What is the search for normal human breast stem cells?
- not able to do lineage tracing but did do cell surface marker analysis
- found that there were four distinct populations
- only one of these, if you transplant back into the mouse fat pad, has the ability to give rise to ductal outgrowths
- same pattern for human and mouse mammary tissue

What are functional similarities between mammary epithelial subpopulations in mouse and human?
- can identify bipotent stem cells in both
- two types of luminal progenitors
- can prospectively isolate all the mature cells as well
- don’t know about all the precursors leading up to myoepithelial cells
- both the mouse and human MaSCs lack receptors for the ovarian hormones oestrogen and progesterone
- important because increased progesterone and oestrogen are linked with increased breast cancer risk
- could they still be influenced?
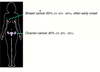
Are MaSCs sensitive to ovarian hormone deprivation?
- yes - highly sensitive
- stem cells appear to retain a ‘memory’ of prior steroid hormone deprivation
- repopulating frequency:
- control: 1/58
- ovariectomy: 1/247
- also when they could generate tissue, it was only very little
What happens to numbers of MaSCs during pregnancy?
- pregnancy is accompanied by an 11-fold increase in the number or activity of MaSCs
- the augmented MaSC pool drives secretory cell expansion
- seen in mid-pregnancy
- transplantation assay measures function
- stem cell highly receptive to hormonal signalling

What is evidence that ovarian hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) profoundly influence stem cell activity?
- hormone deprivation and anti-oestrogens decrease MaSC pool/activity
- excess hormones increase MaSC function
- ageing is associated with increased MaSC function
- pregnancy dramatically increases MaSC pool
- ductal luminal cells express ER and PR - remain the most important prognostic markers for breast cancer to date
- 70% of breast cancers are ER positive and if they are there is a much better prognosis
- how is this signalling to the stem cell when the stem cell doesn’t have receptors for the hormones?

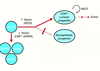
What pathway mediates steroid hormone signalling to stem cells?
- The RANKL/RANK pathway
- signals to NFkB
- steroid hormones like progesterone stimulate ductal cell to make RANKL
- signals to the stem cell pool
- drives proliferation
- probably other molecules involved as well