Lecture 6: Histology of the Esophagus and Stomach Flashcards
What is the innermost layer of the digestive tube and what are its layers?
Mucosa:
Epithelium
Lamina propria
Muscularis mucosae
What’s found in the lamina propria?
- CT
- Lymphatic nodules and immunocompetent cells
- Glands and components of the circulatory system
What is the function of the Submucosa; houses glands in what 2 regions?
- Provides nerve, vascular, and lymphatics supply
- Houses glands in 2 regions: Esophagus and Duodenum
What 2 layers are found within the Muscularis Externa?
1) Inner circular layer of smooth muscle
2) Outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle
What is the outermost layer composed of and where does it differ?
- Serosa in intraperitoneal structures
- Adventitia in retroperitoneal structures
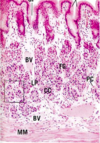
Label the 7 arrows from top to bottom

1) Epithelium
2) Lamina propria
3) Muscularis Mucosa
4) Submucosa
5) Inner circular layer
6) Outer longitudinal layer
7) Serosa
Spinal levels of the: Greater, Lesser, Least, and Lumbar splanchinic nerves?
- Greater = T5-T9
- Lesser = T10-T11
- Least = T12
- Lumbar = L1-L2
Describe the path of the sympathetic branches of the nerves innervating the GI?
Presynaptic nerves which synapse in prevertebral ganglia (celiac, SMG, IMG, aorticorenal), the postsynaptic nerves then travel to organs via blood vessels
What are the 2 parasympathetic nerves for autonomic innervation of the GI; where do they stop and start?
1) Vagus nerve (stops at left colic flexure)
2) Pelvic splanchnics (left colic flexure inferiorly)
Pelvic splanchnics arise from what vertebral levels?
S2, S3, and S4
What are the intrinsic/enteric components of the GI tract innervation?
1) Submucosal plexus of Meissner (in submucosa)
2) Myenteric plexus of Auerbach
Where is the Myenteric plexus of Auerbach located?
Between the inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of the muscularis externa

What is denoted by ‘G’ in this picture?

Submucosal plexus of Meissner

What is denoted by the letter ‘G’ in this picture?

Myenteric plexus of Auerbach

What is the structure that the midde arrow is pointing to?

Myenteric plexus of Auerbach

What does sympathetic vs parasympathetic innervation do to gut motility?
Sympathetic = decreased motility
Parasympathetic = increased motility and secretions
What does the intrinsic/enteric component of the GI do?
- Peristaltic contractions of the ME and movements of muscularis mucosae
- Secretory activities of the muscosal and submucosal glands
What is the best way to identify the different regions of the esophagus, how so?
- Using the Muscularis Externa
Upper 1/3: both layers are striated muscle
Middle 1/3: smooth muscle seen deep to striated
Lower 1/3: both layers are smooth muscle
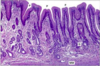
How do you know when you’re looking at the esophageal junction?
Epithelium changes from stratified squamous (esophagus) to simple columnar (stomach)

What is the arrow pointing at?

Gastro-esophageal junction

What is GERD, caused by?
Reflex of acidic contents into the esophagus, irritating the esophageal mucosa
What is this called clinically, caused by?

- Barret Esophagus
- Chronic GERD
- Stratified squamous epithelium replaced by metaplastic columnar epithelium
The normal transition from esophageal stratified squamous epithelium to gastric simple columnar epithelium occrs at which line?
Z-line
Label A-C on the stomach

A) Cardia
B) Fundus
C) Pyloric antrum