Lipids, Proteins & Amino Acids Flashcards
(110 cards)
Functions of Lipids in NATURE
- Energy
- Storage
- Insulation
- Protection
- Transport
- Satiety
- Vitamin absorption
- Essential - nerve cells
Functions of Lipids in INDUSTRY
• Food Science
- Texture
- Flavor
- Aroma
- Heat transfer
• Industry
- Lubricants
- Fuels
- Cosmetics
- Polishes
Dietary Fat Sources (not in SG)
• Animal
- Meat, cheese, dairy, fish
• Plant
- Vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, avocados
• Hidden dietary fat
- Fried foods, baked goods, dressings/sauces
- Combination foods (e.g. pizza & pasta)
Basic Units of Lipids
• Fatty acid
- Hydrocarbon chain
- Stored in triglycerides
- Incorporated in cell membranes (phospholipids)

Fatty Acids
Classified by:
- Length
- Saturation
- Hydrogen position
Methods to classify fatty acids
- Length
- Saturation
- Hydrogen position
Fatty Acids – Chain length classification
- Short: less than 6 carbons
- Medium: 6 - 11 carbons –> coconut oil
- Long: 12 or more carbons
Saturated fatty acids (SFA)
– ID
- Carbons are saturated with hydrogens
- NO double bonds

Saturated Fatty Acids
- Pack tightly together
- Bonding occurs between fatty acids
- Melting point increases
——————|
——————|
——————|
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
– ID
• Hydrogens are replaced by 1 or more double bonds

Monounsaturated Fatty Acid
– ID
• 1 double bond

Monounsaturated Fatty Acid
- Can’t pack tighly
- Low melting point
- Less ability to absorb heat
- Low flash point
• 1 double bond
• Double bond = kink
\————|
/—————|
\—————|
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid
– ID
• 2 or more double bonds

Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid
• 2 or more double bonds
- Can’t pack tighly
- High ability to absorb heat
- High Flash point
• 3 or more double bonds susceptible to oxidation
• many kinks
Cis unsaturated fatty acid
– ID
• H on SAME SIDE of double bond

Cis unsaturated fatty acid
– ID

Trans unsaturated fatty acids
– ID
• H on OPPOSITE SIDE of double bond

Cis vs. Trans fats
– ID
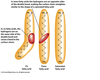
ID the saturated fatty acid
–> 3.

ID the polyunsaturated fatty acid
–> 2.

ID the trans fat
–> 3

Difference between SFA, MUFA, PUFA, cis, and trans fatty acids?
• SFA
Carbons are saturated with Hydrogens, melting point increases, packed tighly together, bonding between fatty acids
• MUFA
1 double bond with Carbons, low melting point, can’t pack tighly togehter
• PUFA
2+ double bonds with Carbons, higher ability to absorb heat, high flash point, 3 or more double bonds are suceptible to oxidation
• Cis
Hydrogens on same side of double bond, kink/bent chain
• Trans
Hydrogens on opposite side of double bond
Saturated Fats in Food
Source
• Solid fats
- Lards, butter, coconut oil, palm oil, cocoa butter
- Animal products
Health Effects of High Intake
- Increased LDL cholesterol
- Increased risk for CVD
Dietary Guidlines
- < 10% of total calories
- < 7% if at risk for CVD
Unsaturated Fats in Food
Food
• Liquids fats
- Olive oil, canola oil, sunflowr oil, peanut oil, sesame oil
• Plants
- Nuts, avocados
• Fish
Health Effects of High Intake
- Incrased HDL cholesterol
- Decreased total & LDL cholesterol
- Decreased CVD risk
Detary Guilines 2010
• 20-35% of daily caloric intake (AMDR)



