Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas Flashcards
(32 cards)
Liver
Gross Anatomy
- Four lobes: right, left, quadrate, caudate
-
Porta hepatis located in concave inferior surface
- branches of hepatic portal vein and hepatic artery enter
- right and left hepatic ducts exit
- lymphatics leave
- Dual blood suppy:
-
Hepatic artery proper
- oxygenated blood
- (Hepatic) Portal Vein
- oxygen poor blood from GI tract, pancreas, and spleen
- Sources mix at liver sinusoids
- Leaves liver via hepatic veins
- Near superior surface of liver
-
Hepatic artery proper
- Covered by mesothelium except in 2 places:
- where directly contacts gallbladder
- bare area where mesothelium → underside of diaphragm
-
Glisson’s capsule
- Dense irregular CT deep to mesothelium
- continuous with capsule around vessels and bile ducts entering liver
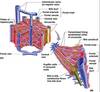
Classic Liver Lobule
Based on venous drainage.
Region whose sinusoids all drain into same centrain vein.
- Hexagonal in cross section
- Portal triads located in portal canals @ each vertex
- Central vein (terminal hepatic venule) @ center
- Blood flows from periphery towards center
- Bile flow from center out

Portal Triad
- Located within portal canal
- Enclosed by the limiting plate of hepatocytes
- Components:
- Hepatic artery/arteriole
- Portal vein/venule
- Bile duct (simple cuboidal epithelium)
- Lymphatic capillaries often present

Central Veins
Terminal Hepatic Venule
- Thin wall with endothelial cells but no smooth muscle
- Plates of hepatocytes organized radially around central vein
- Hepatic sinusoids run between plates
- Receives blood from sinusoids
- Drain into sublobular veins
- Distinguished from portal triad because:
- not accompanied by other vessels/ducts
- less surrouding CT
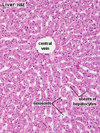
Hepatic Sinusoids
- Highly permeable sinusoidal capillaries
- Wall formed by mixture of endothelial cells and Kupffer cells
- Blood from inlet branches of hepatic artery and portal vein mixes here

Kupffer Cells
- Hepatic resident macrophage
- Contributes to sinusoidal walls
- May extend across lumen
- Phagocytize old/damaged RBC and particulates

Space of Disse
-
Narrow space encircling each sinusoid
- Seperates it from hepatocytes
- Microvilli of hepatocytes extend into space of Disse
- Location of most metabolic exchange between blood and hepatocytes
- Reticular fiber stroma located mainly here

Ito Cells
(Hepatic Stellate Cells)
- Located in the space of Disse
- Stores Vit A in cytoplasmic lipid droplets
- Produces the reticular fiber stroma of liver
- In cirrhosis, produce collagen type I causing fibrosis

Hepatic Blood Flow
Interlobular branches of hepatic artery & portal vein in portal canals →
Distributing branches leave portal canal & run between classic lobules →
Inlet vessels enter lobules →
Sinusoids →
Central vein →
Sublobuler vein →
Larger collecting veins →
3 or more hepatic veins →
IVC
Portal Lobule
Based on bile flow.
Region whose bile canaliculi all drain toward the bile duct in the same portal canal.
- Roughly triangular in cross section
- Central vein at each vertex
- Portal triad in the center
- Bile flows from periphery towards center

Hepatic Acinus of Rappaport
Based on gradients of O2, nutriends, and tonxins supplied by distributing vessels.
Used to explain patterns of hepatocyte metabolism and pathology.
- Diamond shaped in cross section.
- Central veins and portal triads located at the periphery.
- Long axis connects 2 central veins
- Short axis connects 2 portal triads
- Distributing vessels lie on the short axis
- Consists of 3 zones centered around the distributing vessels

Hepatocytes
- Epithelial cells
- Major parenchymal cell of the liver
- LM:
- Polygonal cells with round, euchromatic nuclei
- One or more prominent nucleoli
- Often binucleate or polypoid
- Plasma membrane has 2 structurally and functionally different domains:
-
Sinusoidal domain
- Contacts the space of Disse
- Endocrine face
-
Lateral domain
- Site where bile canaliculi form
- Exocrine face
-
Sinusoidal domain

Bile Canaliculi
- Formed from plasma membranes of adjacent hepatocytes
- Tight junctions prevent bile leakage
- Golgi, lysosomes, and residual bodies of hepatocytes often located near canaliculi
- Lipofuscin may accumulate within residual bodies

Bile Ductules
Intrahepatic ductules, canals of Hering, cholangioles.
- Found near the periphery of a classic lobule
- Lined by simple cuboidal epithelial cells
- Pierce the limiting place
- Drains into interlobular bile ducts
Enterohepatic Recirculation
- Bile salts recirculate between liver and small intestine
- Pathway
- Hepatocyte
- Bile canaliculi
- Bile duct system
- Duodenum
- Some lost in feces
- Resoption into intestinal blood vessels
- Hepatic portal vein
- Hepatic sinusoids
- Space of Disse
- Hepatocyte
Deficiency of Bile Salts
- Can lead to malabsorption of some fats
- Results in steatorrhea
- Precipitation of cholesterol in bile can lead to cholelithiasis
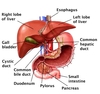
Biliary Tree
- Intrahepatic channels
- Bile canaliculi
- Bile ductules
- Interlobular bile ducts
- Extrahepatic ducts
- Right and left hepatic ducts
- Leave liver at porta hepatis
- Common hepatic duct
- Cystic duct from gallbladder
- Common bile duct
- Right and left hepatic ducts
- Common bile duct unites with the main pancreatic duct
- Forms the ampulla of Vater
- Empties into duodenum at the major duodenal papilla
- sphincter of Oddi

Gallbladder
Functions
- Stores and concentrates bile
- Releases stored bile via cystic duct into common bile duct
-
CCK main stimulus for bile release
- Secreted by I cells in intestinal mucosa
- In response to dietary fat in intestine
- Secreted by I cells in intestinal mucosa
-
CCK main stimulus for bile release

Gallbladder Wall
Has a mucosa, muscularis, and serosa/adventitia.
No muscularis mucosae or submucosa.
-
Mucosa
-
Simple columnar epithelium
- mainly absorptive cells
- lateral spaces between absorptive cells widen when actively concentrating bile
- Lamina propria
- Unless gallbladder is full, mucosa usually has many deep irregular folds
-
Simple columnar epithelium
-
Muscularis
- Circular near neck of bladder
- More irregular in body
-
Serosa/Adventitia
- Adventitia is present where gallbladder directly contacts liver
- Serosa covers remainder of the organ

Rokitansky-Aschoff Crypts
- Deep invaginations of the epithelium
- Extends into or through muscularis
- Found in the gallbladder with chronic inflammation
- May perforate

Pancreatic Acinar Cells
- Pyramid-shaped serous cells
- Secrete wide variety of digestive enzymes zymogens
- Trypsinogen
- Chymotrypsinogen
- Procarboxypeptidase
- Basal basophilia due to extensive RER
- Acidophilic zymogen granules in apical cytoplasm stores enzymes
-
Exocytosis occurs in response to signals
- CCK
- ACh from vagal fibers

Centroacinar Cells
- Pale, low cuboidal cells
- Unique to the pancreas
- Lies within the lumen of a secretory acinus
- Represents the first cells in an intercalated duct
- Intra-acinar portion

Pancreatic
Intercalated Ducts
- Smallest type of intralobular duct
- Simple, low cuboidal epithelium
- Secretes a watery bicarbonate-rich fluid
- In response to secretin
- Hormone produced by S cells in duodenum
- In response to secretin
- Drains into larger intralobular ducts

Pancreatic Ductal System
- Centroacinar cells → first cells in an intercalated duct
- Intercalated ducts
-
Larger intralobular ducts
- Lined by simple cuboidal epithelium
-
No basal striations
- No striated duct in the pancreas
- Empty into interlobular ducts
-
Interlobular ducts
- Run in the CT septa
- Empty into the main pancreatic duct
-
Main duct
- Units with common bile duct
- Form the ampulla of Vater
- Empties into duodenum at the major duodenal papilla







