Lower Extremities Flashcards
(87 cards)
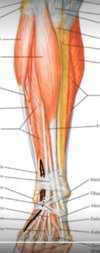
Name the components of the anterior compartment of the lower leg.
Extensor muscles: 1.) tibialis anterior 2.) extensor digitorum longus 3.) extensor hallucis longus 4.) fibularis (peroneus) tertius Anterior tibial artery and veins Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve [Plate 510]
Name the components of the lateral compartment of the lower leg.
Fibularis (peroneus) longus muscle Fibularis (peroneus) brevis muscle Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve [Plate 510]
Name the components of the superficial posterior compartment of the lower leg.
Superficial flexor muscles: Soleus Gastrocnemius Plantaris (tendon) [Plate 510]
Name the components of the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg.
Deep flexor muscles: Flexor digitorum longus Tibialis posterior Flexor hallucis longus Popliteus Posterior tibial artery and veins
Name the 4 muscles which make up the quadriceps femoris (from lateral to medial)
- Vastus lateralis
- Rectus Femoris
- Vastus intermedius (deep to rectus femoris)
- Vastus medialis
Name the muscles which comprise the anterior thigh muscle group.
From lateral to medial
- Quadriceps:
- vastus lateralis
- rectus femoris
- vastus intermedius
- vastus medialis
- Sartorius
- IIiopsoas

origin of the vastus medialis
intertrochanteric line, medial lip of linea aspera of femur [From Netter’s Anatomy, Table 7]
insertion of the vastus medialis
base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament [From Netter’s Anatomy, Table 7]
innervation of vastus medialis
femoral nerve [From Netter’s Anatomy, Table 7]
main action of vastus medialis
extends leg at knee joint [From Netter’s Anatomy, Table 7]
blood supply of vastus medialis
femoral and profunda femoris arteries
origin of the vastus lateralis
greater trochanter, lateral lip of linea aspera of femur
insertion of the vastus lateralis
base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
innervation of the vastus lateralis
femoral nerve
main action of the vastus lateralis
extends leg at knee joint
blood supply of the vastus lateralis
lateral circumflex femoral and profunda femoris arteries
origin of the vastus intermedius
anterior and lateral surfaces of body of femur
insertion of the vastus intermedius
base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
innervation of the vastus intermedius
femoral nerve
main action of the vastus intermedius
extends leg at knee joint
blood supply of the vastus intermedius
lateral circumflex femoral and profunda femoris arteries
The ________ ________ is the only extensor of the knee joint.
quadriceps femoris [From https://www.kenhub.com/en/videos/vastus-medialis-3d-anatomy]
What does musculus rectus femoris mean?
straight muscle of the thigh [From https://www.kenhub.com/en/videos/rectus-femoris-muscle-3d-anatomy]
The femoral nerve originates from the lumbar plexus, specifically the ________ ____ of the ___ through ___ lumbar nerves.
anterior rami 2nd through 4th lumbar nerves [From https://www.kenhub.com/en/videos/rectus-femoris-muscle-3d-anatomy]