LS 7B Flashcards
(236 cards)
How do most cancers arise?
A. from a single mutations arising simultaneously in a cluster of cells
B. from a series of mutations that arise in the descendants of a single somatic cell
C. from multiple mutations arising simultaneously in a single cell
D. from mutations arising in a single cell that are then transmitted to other cells in the body
B. from a series of mutations that arise in the descendants of a single somatic cell
How do mutations arise?
A. Mutations in cancer cells arise because they need to divide faster.
B. Mutations arise in a specific sequence where a mutation in one gene directly leads to a mutation in a specific second gene.
C. Mutations arise randomly and independent of other mutations in the cell.
D. Mutations arise simultaneously, where whole sets of mutations occur in a single event.
C. Mutations arise randomly and independent of other mutations in the cell.
What effect does each successive mutation have on the colon cells in the example?
A. It causes them to leave the colon and spread to other tissues.
B. It causes them to divide more rapidly than normal cells.
C. It causes them to become non-colon cells.
D. In causes them to become larger and expand in the colon.
B. It causes them to divide more rapidly than normal cells.
When p53 becomes mutant in cells already mutant for APC and Ras, what occurs?
A. These cells survive despite DNA damage and divide extremely rapidly.
B. These cells die.
C. These cells remain benign.
D. These cells expand their chromosome number to 53.
A. These cells survive despite DNA damage and divide extremely rapidly.
According to Figure 14.2, the average number of new mutations that occur across an entire human genome in one generation is approximately _____ times higher than in nematodes.
A. 100
B. 1000
C. 10
D. 10,000
E. 2

A. 100
The number of new mutations in organisms following a round of genome replication:
A. generally decreases with larger genomes.
B. generally increases with larger genomes.
C. None of the answer options is correct.
D. is highest in bacteria.
E. is similar, independent of genome size.
B. generally increases with larger genomes.
Sites in the genome that are more susceptible to mutations than others are called:
A. risk factors.
B. genes.
C. mutation spots.
D. hotspots.
E. noncoding DNA.
D. hotspots.
_____ mutations are important to the evolutionary process; most cancers result from _____ mutations.
A. Somatic; germ-line
B. Germ-line; heritable
C. Somatic; heritable
D. Point; germ-line
E. Germ-line; somatic
E. Germ-line; somatic
Which of the following statements concerning cancer and mutations is CORRECT?
A. Cancer can only occur with a mutation in a somatic cell.
B. Usually, multiple mutations are required in different genes to cause cancer.
C. Usually, a single mutation is all that is required to cause cancer.
D. Cancer can only occur with a mutation in a germ cell.
E. None of the other answer options is correct.
B. Usually, multiple mutations are required in different genes to cause cancer.
The definition of mutation is “any heritable change in the genetic material.” The qualifier “heritable” is necessary because:
A. most changes in the genetic material are harmful to the organism.
B. changes in the genetic material occur without regard to the needs of the organism.
C. changes in the genetic material occur at random along the genome.
D. most changes in the genetic material are repaired soon after they occur.
D. most changes in the genetic material are repaired soon after they occur.
Prophase of meiosis I has some important differences from prophase of mitosis. These differences include: ___________ pair, and _________ occurs.
A. chromatids; condensation
B. chromosomes; separation
C. homologous chromosomes; crossing over ,
D. homologous chromatids; separation
C. homologous chromosomes; crossing over
During meiosis crossing over takes place between:
A. any two chromatids.
B. sister chromatids.
C. non-sister chromatids.
D. nonhomologous chromosomes.
E. nonhomologous chromatids.
C. non-sister chromatids.
In this partial image of anaphase I of meiosis, most of a chromosome is shaded dark, whereas a portion of what is in the circle is shaded light. Which of the following statements best explains the meaning of this shading?
A. The dark and light indicate homologous chromosomes.
B. The light part came from the homolog by crossing over.
C. The light part is a mixture of genes from both parental types.
D. The light and dark parts are different genes.

B. The light part came from the homolog by crossing over.
In the image below, let the light shade indicate maternally derived chromosomal material and the dark shade indicate paternally derived material. Which circle is likely to contain both paternal and maternal gene variants (alleles)?
A. circle a
B. circle b
C. circle c
D. circle d

B. circle b
In the figure below, which box encloses two copies of the same gene variants (alleles) from only one of the parents?
A. box a
B. box b
C. box c
D. box d
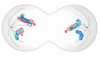
C. box c
In the figure below, which box encloses gene variants (alleles) of the same genes from both parents?
A. box a
B. box b
C. box c
D. box d

B. box b
In the figure below, which box contains only single gene copies from one of the parents?
A. box a
B. box b
C. box c
D. box d

A. box a
In the figure below, which box contains some gene variants (alleles) from one parent and some from the other, but not variant alleles from the same gene?
A. box a
B. box b
C. box c
D. box d

D. box d
Which of the following is NOT true about gametes?
A. They are genetically identical to other gametes formed during meiosis.
B. They fuse to form a new organism during fertilization.
C. They have half as many chromosomes as a somatic cell of the same individual.
D. They are formed by meiotic cell division.
E. They are called eggs and sperm in animals.
A. They are genetically identical to other gametes formed during meiosis.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of meiotic cell division?
A. Cell division results in the production of gametes.
B. Daughter cells are genetically identical.
C. Cell division requires two rounds of nuclear division.
D. Cell division results in the formation of four daughter cells.
B. Daughter cells are genetically identical.
When do sister chromatids separate in meiosis?
A. anaphase I
B. metaphase II
C. telophase I
D. anaphase II
D. anaphase II
Homologous chromosomes separate from each other in:
A. meiosis I.
B. mitosis.
C. They never separate from each other during any form of cell division.
D. meiosis II.
A. meiosis I.
In a population of organisms with 4 alleles, how many homozygous genotypes are possible? How many heterozygous genotypes are possible?
A. 3; 4
B. 4; 3
C. 4; 4
D. 4; 6
E. 4; 10
D. 4; 6
Consider a gene with four alleles A1, A2, A3, and A4. How many distinct heterozygous genotypes are possible?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
E. 6
E. 6









































