Midterm 3 structure Flashcards
1
Q

A
Methadone
2
Q

A
Ceftaroline Fosamil Acetate
- Effective against gram + and -
- Exhibit Activity against MRSA
- Bacterial Cell wall synthesis inhibitor
3
Q

A
Fludrocortisone
Mineralocorticoids
4
Q

A
Prednisolone
- Glucocorticoid
- Regulate glucose metabolism
- Anti-inflammatory activity
- Glucose sparing effect
5
Q

A
Prednisone
6
Q

A
Ciprofloxacin
- Quinolone : inhibit DNA synthesis by promoting cleavage of bacterial DNA in the DNA gyrase
- Effective against gram - (inhibition of DNA gyrase) and gram + (inhibition of DNA type 4 topoisomerase)
- conc dependent killing + PAE / Bactericidal Activity
- used with caution in patients with epilepsy/seizures
- Photosensitivity; rash; tendonitis; prolong QT; Chelation with antacids
- Not safe for children/pregnant women (CAT.C)
7
Q

A
Tigecycline
- Glycylcycline
- Inhibits protein synthesis
- IV only
- Cat. D
- Teeth staining in children less than 8 yrs
8
Q

A
Naproxen
- NSAID
- Non-Selective Cox inhibitors - slightly selective for COX 1
- Analgesic, Antipyretic, Anti-inflammatory
- Longer duration of action than Ibuprofen
9
Q

A
Hydrocodone
10
Q

A
Sulfamethoxazole
- Competitive inhibitor of PABA
- Antimetabolite -> prevent folate synthesis
- Synergistic with trimethoprim
- Gram + and - ive
- MRSA
11
Q
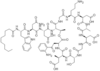
A
Daptomycin
- Lipopeptide
- Binds to bacterial membrane by a Ca++ dependent mechanism –> depolarization, K efflux & cell death
- Not for treatment of pneumonia
- Skeletal muscle myalgia & weakness
- Cleared renally
- Concentration-dependent Killing
- active against vancomycin resistant strains of enterococci and staphylococci.
12
Q

A
Vancomycin
- Glycopepetide
- Inhibits Cell Wall Synthesis by binding to the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of nascent peptidoglycan
- Nephortoxicity & ototoxicity (when combined with aminoglycosides)
- Skin rash
- Redman Syndrome if rapid IV infusion
- Gram +
13
Q

A
Naloxone
- pure antagonist
- Antagonists at mu & kappa receptors
- Treat opioid overdose
- Rescue agent for respirator depression
14
Q

A
Meperidine
- Agonist - pure phenylpiperidine
- Metabolized to normeperidine, which may cause seizures at high plasma levels
- SS when usd with SSRIs
- Hyperpyrexic coma when used with MAO inhibitors (Linezolid)
15
Q

A
Gentamycin
- Aminoglycosides - bacteria origin
- Gram - aerobic bacteria
- Renal Clearane
- Synergistic with beta-lactams or vacomycin against gram +
- Oto and Nephro-toxicity
- Bacterial protein Synthesis (binding to the 30S Ribosomal subunit)
16
Q

A
Cephalexin
- 1st gen Cephalosporin
- Impaired cell wall synthesis
- Treat skin and soft tissue infection ; UTI
- Time dependent Killing
- DDI alcohol : disulfiram
- DDI Probenecid –> Tubular secretion
- Should not be used with pts who has penicillin allergies
17
Q

A
Capecitabine ( Xeloda)
18
Q

A
Oxycodone
- Agonist - Pure Phenanthrenes
- Genetic in certain hepatic enzymes (CYP 2D6)
- Strong Agonist ( mu receptor)
- Heptatic Metabolism
- Toxicities : Respiratory depression, constipation, addiction liability
19
Q

A
Oxymorphone
- Strong Agonist ( mu receptor)
- Heptatic Metabolism
- Toxicities : Respiratory depression, constipation, addiction liability
20
Q

A
Meropenem
- Carbapenems (IV)
- Low susceptibility to Beta-Lactamase
- Gram + and - Anaerobic ; slightly greater activity against gram - aerobic
- Prevent cell wall synthesis by binding and inhibiting cell wall transpeptidases
- Less likely to cause seizures than Imipenem
21
Q

A
Auranofin
DMARD (gold complex)
22
Q

A
Oxaprozin
- NSAID
- Highly photosensitive
23
Q

A
Aztreonam
- Monolactam - for patients with penicillin allergies
- Synergistic with aminoglycosides
- IV only
- Prevents bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to and inhibiting cell wall transpeptidases (bind to PBP)
- Eliminated via renal tubular secretion (half life is prolonged in renal failure)
- Works against gram - aerobes; No activity against gram + or anaerobes
24
Q

A
Clindamycin (Lincosamide)
- anaerobic antibiotic and gram + aerobic antibiotic; not effective against gram - aerobes
- activity against many MRSA.
- drug and metabolites are eliminated by biliary and renal excretion.
- Prevents bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit
- Skin and soft tissue infections, anaerobic infections
- Toxicity: Gastrointestinal upset, difficile colitis.
- Undergoes hepatic metabolism
- Semisynthetic - bacteriostatic
25

Cefamandole
* Second Gen Cephalosporins
* Works against anaerobes; extended gram - aerobes
* treats Sinus, ear, and respiratory infections cause by H. influenzae or M.Catarrhalis
26

Metronidazole
* Nitroimidazole
* Disrupt Electron transport (MoA)
* Bactericial against anaerobic
* Used infections caused by C.Difficile Colitis; can be used for moderate MRSA
* GI upsets, Metallic taste, Neuropathy
* DDI with alcohol : Disulfiram like rxns


