MSK 3 Flashcards
(86 cards)
Temporomandibular Joint: Normal range of motion test
3 finger insert test
1
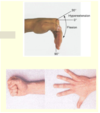
- __________ are hard, bony outgrowths or gelatinous cysts on the proximal interphalangeal joints (the middle joints of fingers or toes.)
- Sign of ___________

Bouchard’s nodes=PIP
Osteoarthritis

2
- _________ are hard or bony swellings that can develop in the distal interphalangeal joints (DIP) (the joints closest to the end of the fingers and toes)
- Sign of ___________

- Heberden’s nodes=DIP
- Osteoarthritis

1
- It results from hyperflexion of the extensor digitorum tendon
- Injury of the extensor digitorum tendon of the fingers at the distal interphalangeal joint
- Usually occurs when a ball, while being caught, hits an outstretched finger and jams it
- Inability to extend finger

Mallet Finger
Hyperflexion at DIP (extensor digitorum tendon)

2
- Presents with flexion of the PIP and hyperextension of the DIP.
- PIP=flexion
- DIP=hyperextension
- May affect one or more fingers, including the thumb.
- Active flexion results in being “stuck” until person passively extends finger
- PIP joint will not straightened under its own power (actively) but can be straightened by the other hand (passively). In addition the end joint of the finger (DIP joint) over straightens and will not bend (flex) fully.
- Keyword: “POP”
- Generally caused by a forceful blow to the top (dorsal) side of a bent (flexed) middle joint of a finger or a deep cut.
- May also be caused by Rheumatoid arthritis

Boutonniere (“button hole”) deformity/Trigger finger

3
- Develops with hyperextension of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint and flexion of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint.
- PIP=hyperextension
- DIP=flexion
- May affect one or more fingers but not the thumb.
- Occurs in about 50 per cent of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cases

Swan-neck deformity

“Squeeze-Test” (MTP/MCP)
- Indicates Rheumatoid arthritis
- Positive squeeze test – where squeezing the hand across the knuckle joints is unduly painful

Signs of Rheumatoid arthritis

- grating, crackling or popping sounds and sensations experienced in the joints or a crackling sensation
- Indication of lost cartilage (sound is bone on bone)
- crepitus
- __________ and _________ will likely display crepitus
- Also common in trauma and is a common sign of ________
- osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- bone fracture
- Presence of increased intra-articular fluid (fluid in the joint)
- Can be blood, synovial fluid, or gout fluid
Joint Effusion
Palpate for warmth utilizing the ____ of the hand
dorsum
Shoulder range of motion
- flexion (180 degrees)
- extension (50 degrees)
- abduction (180 degrees)
- adduction (50 degrees)
- internal rotation (90 degrees)
- external rotation (90 degrees)
(ball and socket joint)

Degree of normal range of motion:
- shoulder flexion
180 degrees
(same as abduction)

Degree of normal range of motion:
- shoulder hyperextension
50 degrees
(same as adduction)

Degree of normal range of motion:
- shoulder abduction
180 degrees
(same as flexion)

Degree of normal range of motion:
- shoulder adduction
50 degrees
(same as hyperextension)

Degree of normal range of motion:
- shoulder external rotation
90 degrees

Elbow range of motion
- Flexion (160 degrees)
- Extension (180 degrees)
- Pronation (90 degrees)
- Supination (90 degrees)

Degree of normal range of motion:
- Elbow flexion
160 degrees

Degree of normal range of motion:
- Elbow extension
180 degrees

Degree of normal range of motion:
- Elbow supination
90 degrees

Degree of normal range of motion:
- Elbow pronation
90 degrees

Degree of normal range of motion:
- shoulder internal rotation
90 degrees