Muscloskeletal Radiology Slides Flashcards
(29 cards)
Side (sagittal) + Frontal (coronal) view of:

Normal Right Shoulder
& Rotator cuff
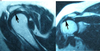
Sagittal + Coronal (front) view of:

Right shoulder with rotator cuff tear
(in supraspinatus tendon)
- white area above humeral head = fluid resulting from rotator cuff tear*
- black structure next to humeral head (@2 o’clock) = retracted end of torn supraspinatus tendon*

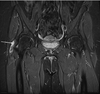
What is injured in this MRI?


SLAP tear: Superior Labrum Anterior & Posterior
- Labrum: a ring of fibrocartilage (fibrous cartilage) around the edge of the articular (joint) surface of a bone
What type of tumor is this?
What is the defining feature?

osteosarcoma of proximal humerous
feature: :moth-eaten” edges

What type of dislocation is shown?
Is this common?

anterior dislocation
of humerous (resides in front of glenoid)
- common
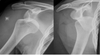
What type of dislocation is shown?
Is this common?

Posterior dislocation, humerus
(head resides behind glenoid fossa)
- rare

What injury is shown?

humeral fracture
(neck of humerous)

What type of fracture is this?
What nerve could be damaged?
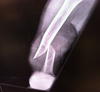
Midshaft humeral fracture
- radial nerve
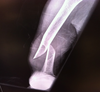
What type of fracture is this?
What 2 types of this fracture can occur?

distal humeral fracture (condylar)
- can be supracondylar or condylar

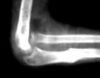
What type of elbow dislocation is this?
What are all the possible types?

posterior elbow dislocation
- posterior
- anterior
- lateral
- medial
- divergent

What is this injury know as?
What does it consist of?

Terrible Triad
- elbow dislocation
- radial head fracture
- coronoid fracture
What 2 types of MRI imaging are seen here?

left: T1
right: T2

What type of fracture is this?

metaphyseal fracture
(does NOT effect growth plate)

What type of fracture is this?

Torus or “buckle” fracture
- topmost layer of bone on one side of the bone is compressed, causing the other side to bend away from the growth plate

What type of fracture is this?

Greenstick
- one bone fractures causing the other to bend

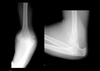
This type of fracture is common in the arms of children:
(fracture in ulna; radius is dislocated)

Monteggia fracture
This type of fracture is common in the arms of children:
(fracture in radius; ulna is dislocated)
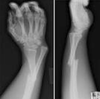
Galeazzi fracture
This fracture occurs across or at the growth plate:

Salter fractures or Physeal fracture

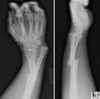
In these 2 wrist fractures the wrist bone slides over or under the ulna + radius. Identify the fractures in the top and bottom images.

top: Colles (wrist = over)
bottom: Smith (wrist = under)

Name this fracture fo the 5th metacarpal bone:

Boxer Fracture

This fracture causes Pain in the snuffbox:
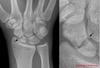
Scaphoid fracture

This is a stable type of pelvis fracture:

acetablar fracture
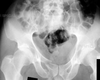
This is a penis…I mean..uh.. unstable type of pelvic fracture:

Open book
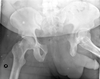
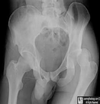
What is wrong in this image?
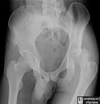
Posterior hip dislocation